Southern Canadian Rockies Map
Mount Assiniboine Region
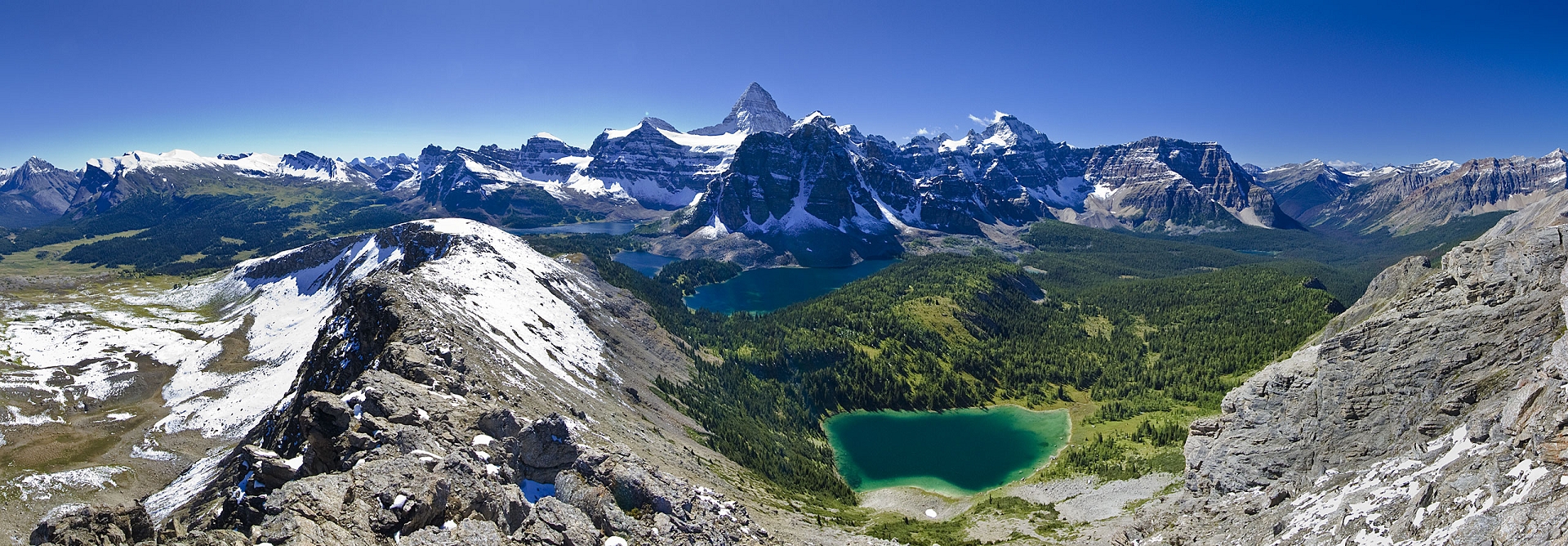
Mount Assiniboine Panoramic
Jeffrey Pang (Wikipedia)
![]()
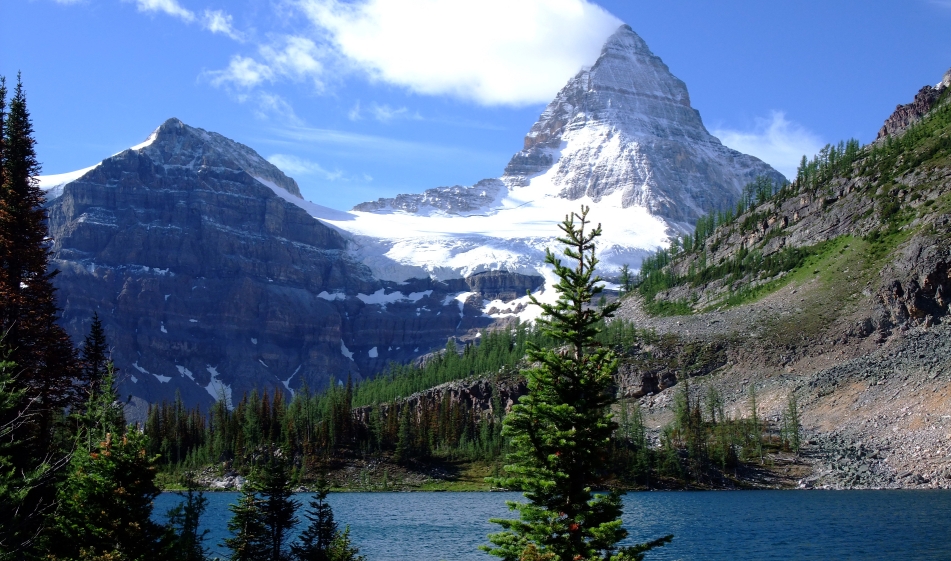
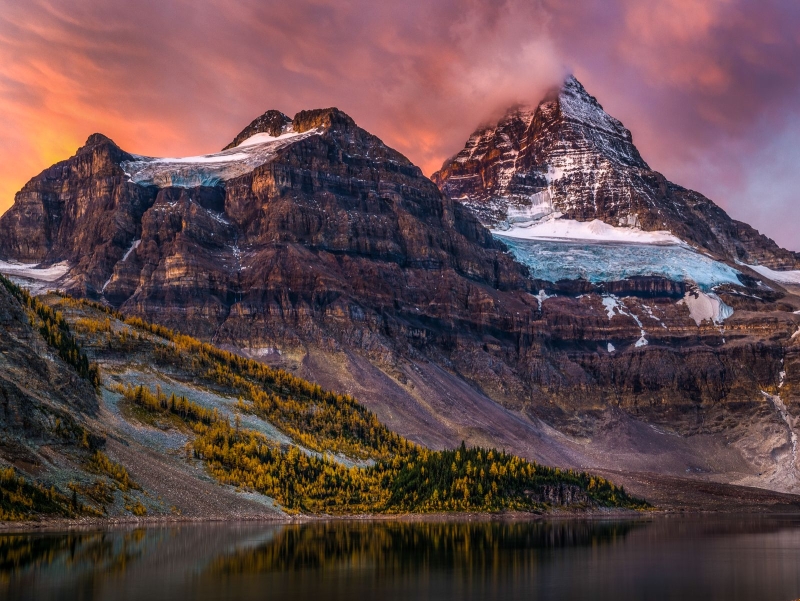
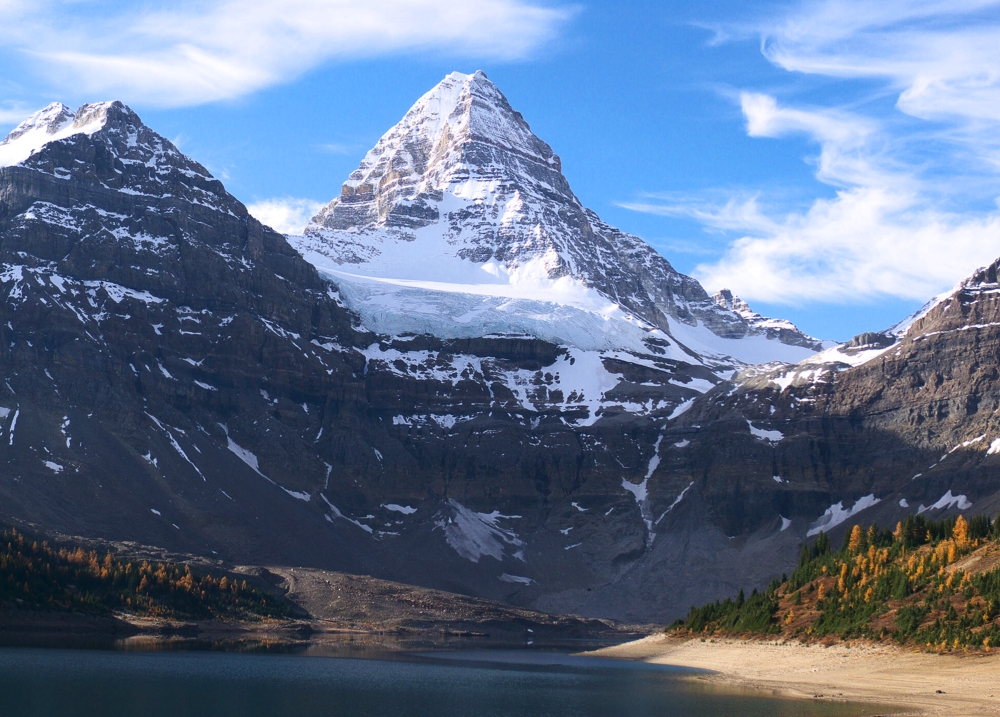
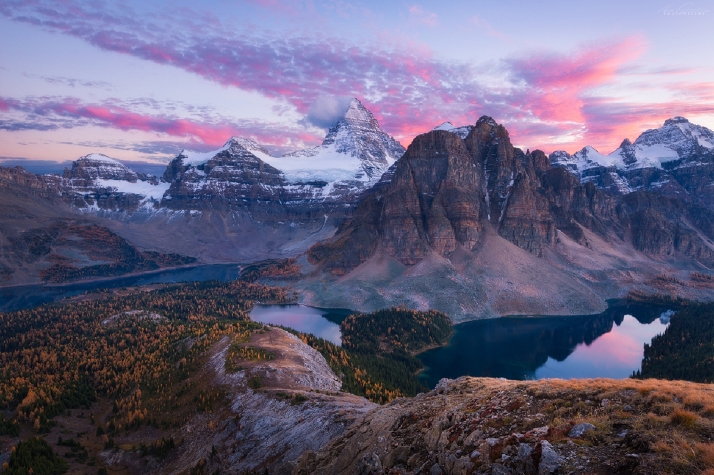
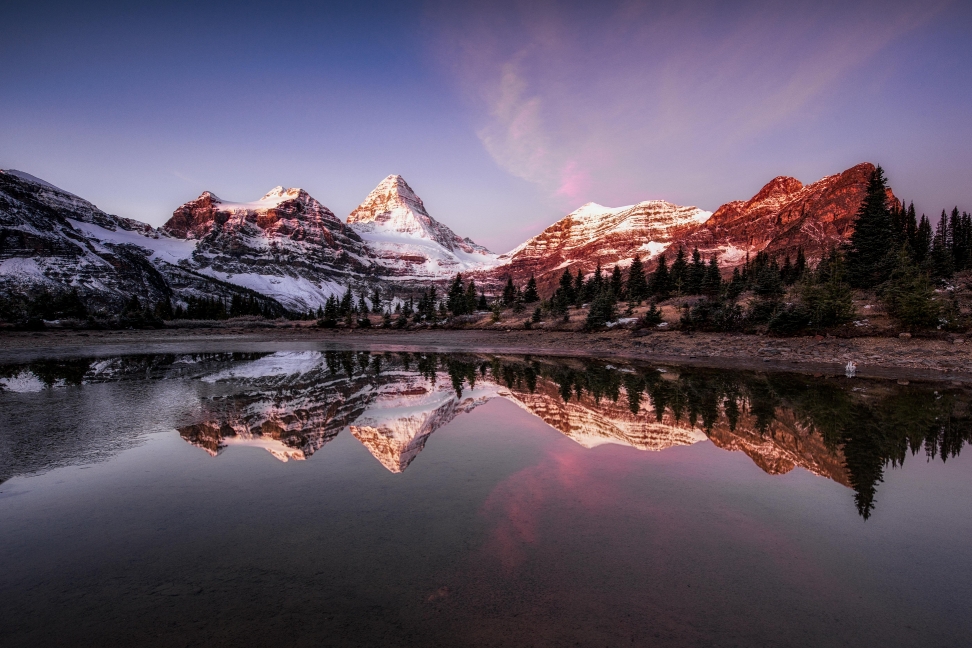
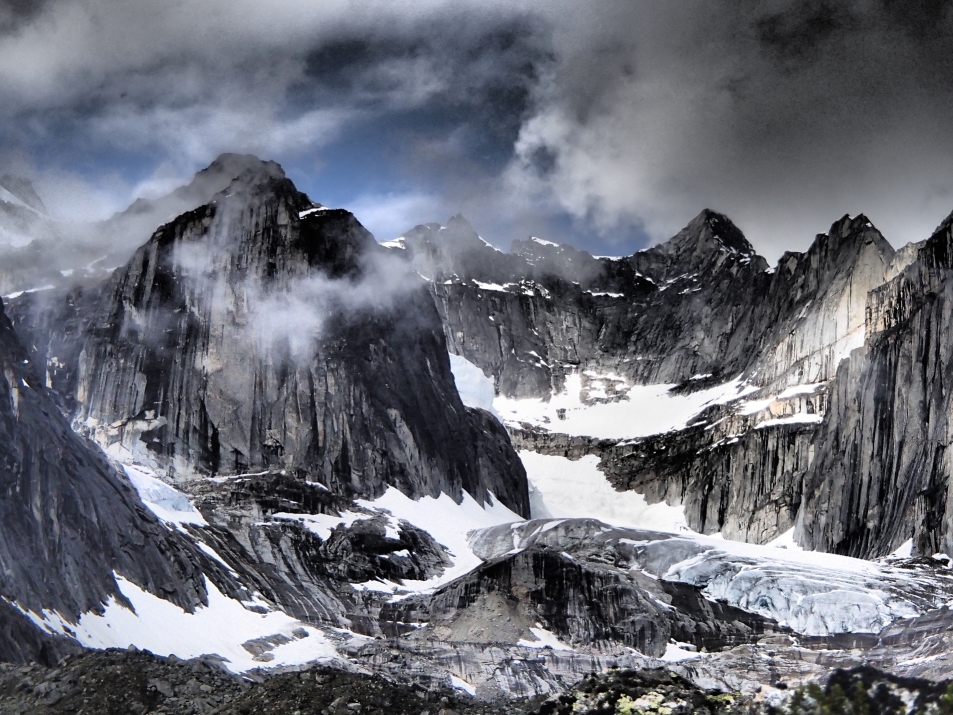
Mount Assiniboine, also known as Assiniboine Mountain, is a pyramidal peak mountain on the Great Divide, on the British Columbia/Alberta border in Canada.
At 3,618 m (11,870 ft), it is the highest peak in the Southern Continental Ranges of the Canadian Rockies. Mount Assiniboine rises nearly 1,525 m (5,003 ft) above Lake Magog. Because of its resemblance to the Matterhorn in the Alps, it is nicknamed the “Matterhorn of the Rockies”.[5]
Mount Assiniboine was named by George M. Dawson in 1885. When Dawson saw Mount Assiniboine from Copper Mountain, he saw a plume of clouds trailing away from the top. This reminded him of the plumes of smoke emanating from the teepees of the Assiniboine people.[1]
Mount Assiniboine lies on the border between Mount Assiniboine Provincial Park, in British Columbia, and Banff National Park, in Alberta.[6] The mountain can be reached only by a six-hour hike or horse-pack 27 km (17 mi), three-hour bike ride (now disallowed to reduce human / grizzly encounters) or helicopter.
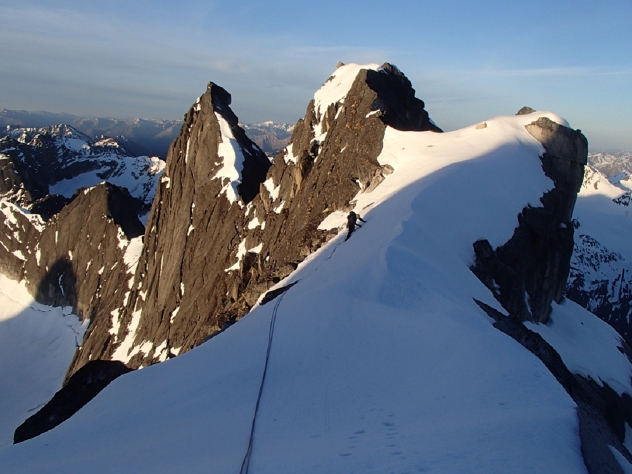
Climbing
Mt. Assiniboine was first climbed in the summer of 1901 by James Outram, Christian Bohren and Christian Hasler.[4] In 1925, Lawrence Grassi became the first person to make a solo ascent. On August 27, 2001, Bohren’s granddaughter Lonnie along with three others made a successful ascent, celebrating the 100th anniversary of the first ascent.[1]
There are no scrambling routes up Mt. Assiniboine. The easiest mountaineering routes are the North Ridge and North Face at YDS 5.5 which are reached from the Hind Hut.
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article Mount Assinboine, which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike 4.0 International License (view authors).
Tonsa Peak / Mount Tuzo Region

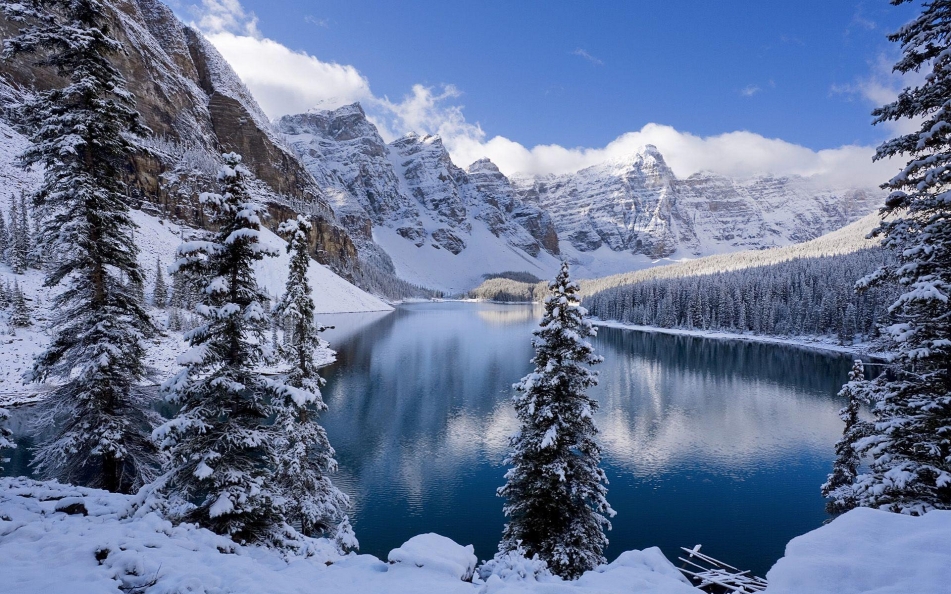
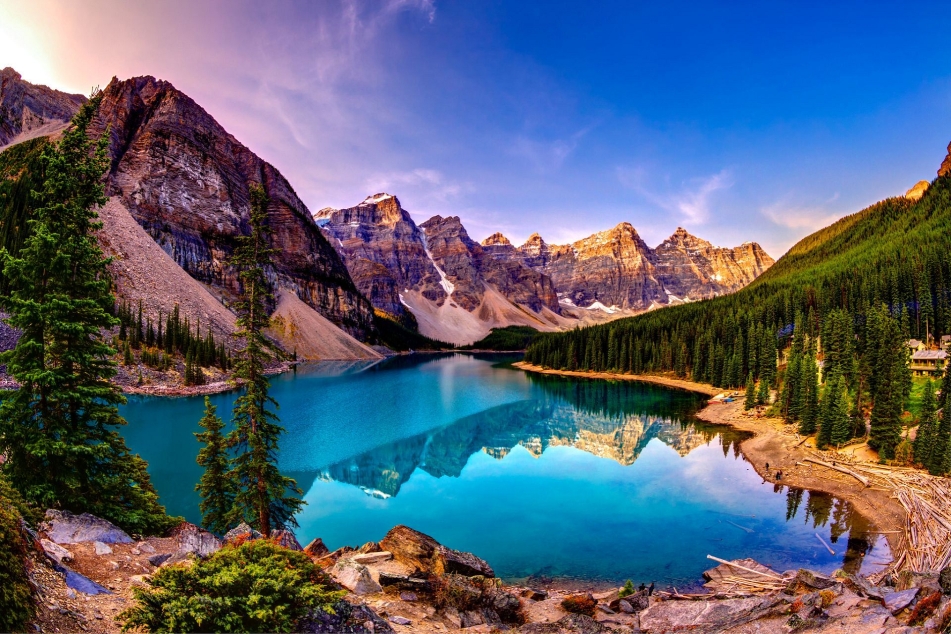
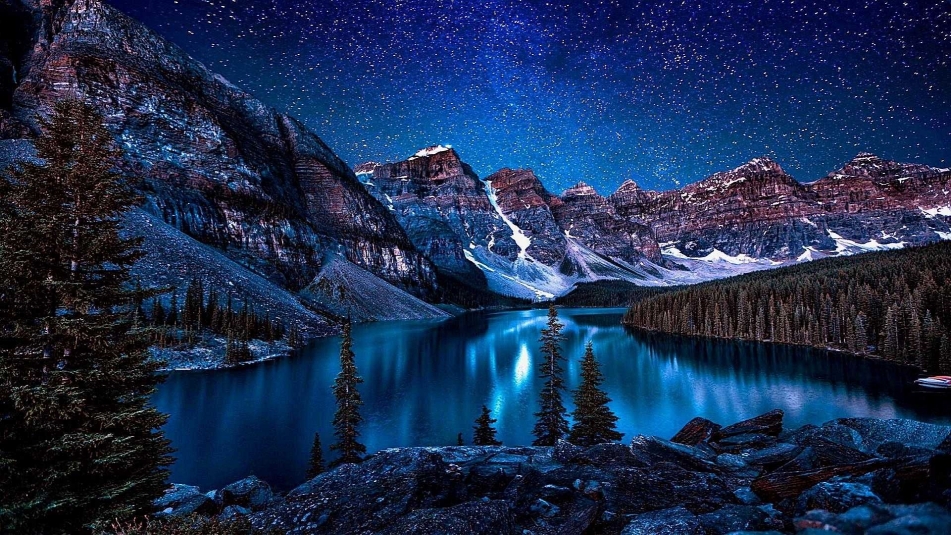
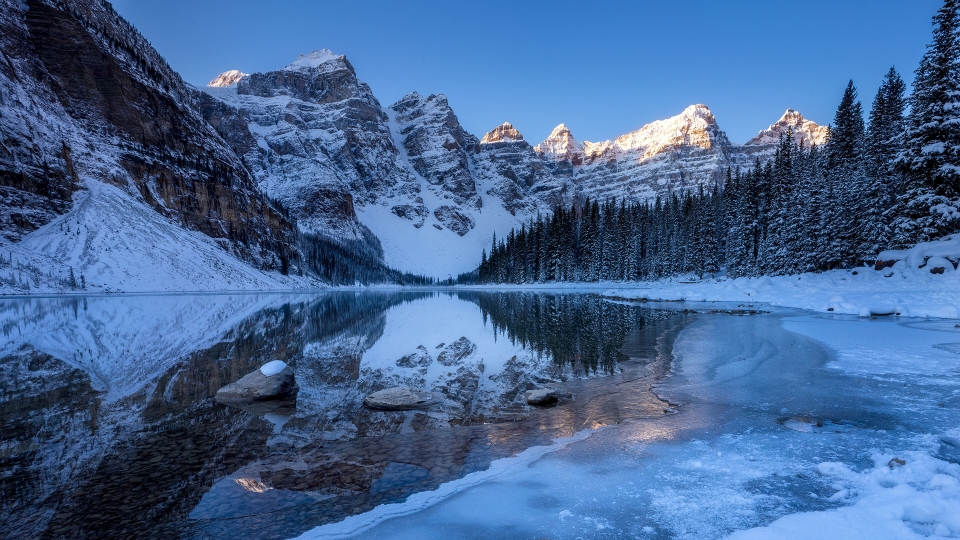
Tonsa, or Tonsa Peak, is a 3,053-metre (10,016 ft) mountain summit located on the border of Alberta and British Columbia on the Continental Divide in the Canadian Rockies. The mountain forms part of the backdrop to Moraine Lake in the Valley of the Ten Peaks of Banff National Park. It was named in 1894 by Samuel E.S. Allen for the Stoney Indian word for the number four. [2]
Geology
Like other mountains in Banff Park, Tonsa is composed of sedimentary rock laid down during the Precambrian to Jurassic periods.[3] Formed in shallow seas, this sedimentary rock was pushed east and over the top of younger rock during the Laramide orogeny.[4]
Mount Tuzo is a mountain located within the Valley of the Ten Peaks in the Canadian Rockies, along the Continental Divide, which forms the provincial boundary between British Columbia and Alberta in Western Canada.[1][3][5] It also lies on the boundary shared by Banff National Park and Kootenay National Park.
The mountain was named in 1907 after its first ascendant, Henrietta L. Tuzo. Tuzo was a charter member of the Alpine Club of Canada.[5][3] On his 1894 map, Samuel Allen had named the peak “Shagowa”, which is the Nakoda word for seven as the mountain is seventh in order from south to north of the ten peaks.[3]
This article uses material from the Wikipedia articles Tonsa and Mount Tuzo, which are released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike 4.0 International License (view authors here and here).

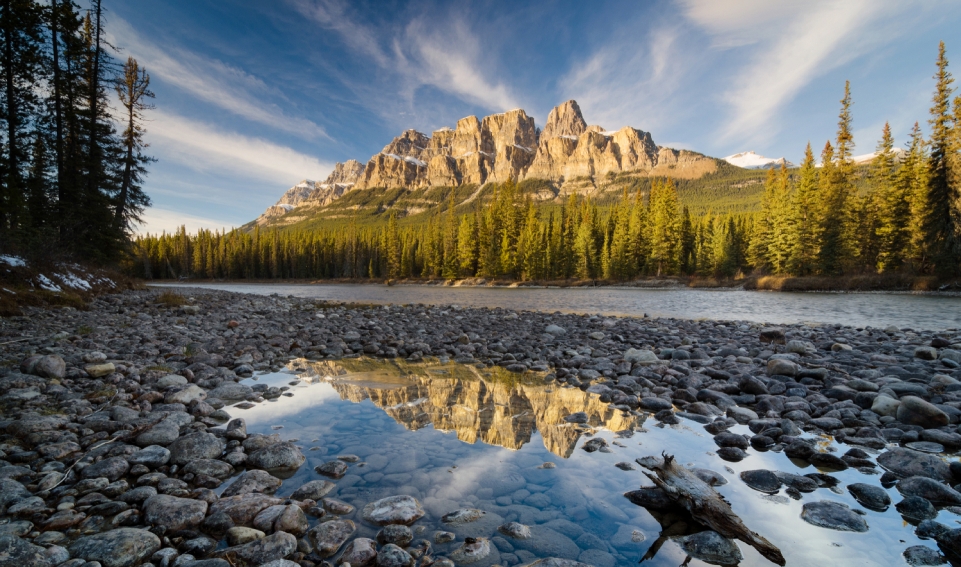
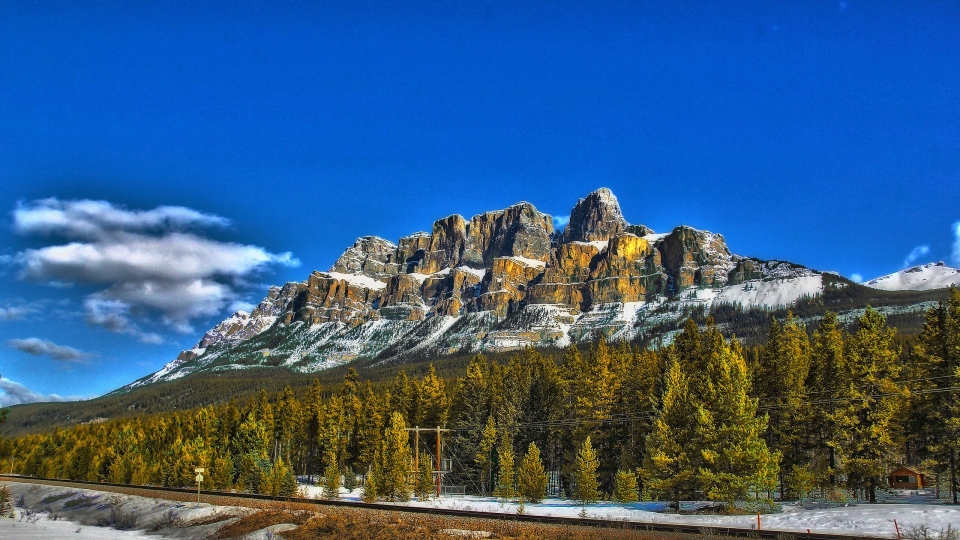
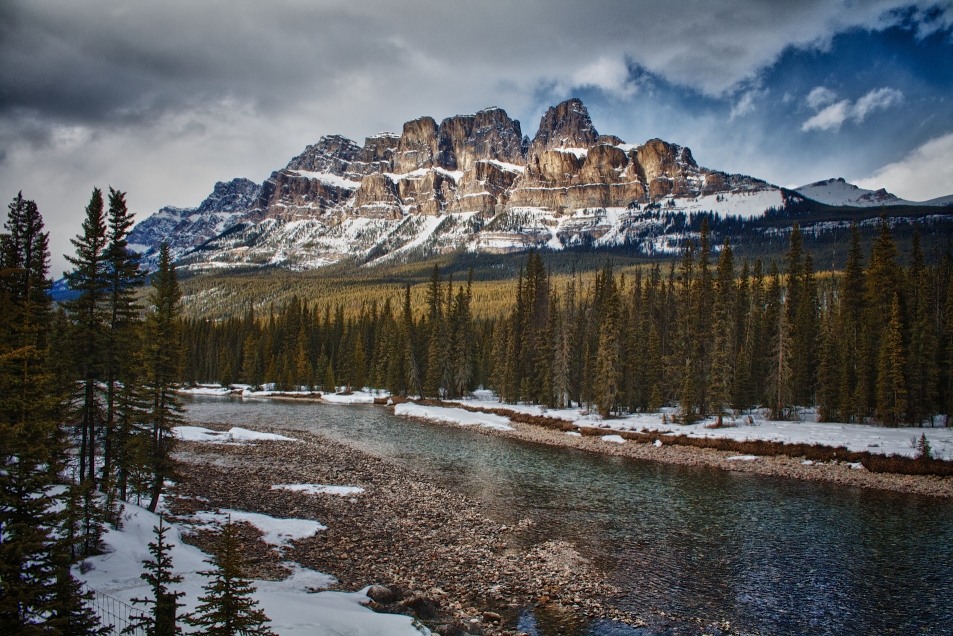
Castle Mountain (Blackfoot: Miistukskoowa) is a mountain located within Banff National Park in the Canadian Rockies, approximately halfway between Banff and Lake Louise. It is the easternmost mountain of the Main Ranges in the Bow Valley and sits astride the Castle Mountain Fault which has thrust older sedimentary and metamorphic rocks forming the upper part of the mountain over the younger rocks forming its base. The mountain’s castellated, or castle-like, appearance is a result of erosive processes acting at different rates on the peak’s alternating layers of softer shale and harder limestone, dolomite and quartzite.
The mountain was named in 1858 by James Hector for its castle-like appearance. From 1946 to 1979 it was known as Mount Eisenhower in honour of the World War II general Dwight D. Eisenhower. Public pressure caused its original name to be restored, but a pinnacle on the southeastern side of the mountain was named Eisenhower Tower. Located nearby are the remains of Silver City, a 19th-century mining settlement, and the Castle Mountain Internment Camp in which persons deemed enemy aliens and suspected enemy sympathizers were confined during World War I.
While looking nearly inaccessible from the Trans-Canada Highway, the peak can be ascended from the backside on the northeastern slopes. The trail to Rockbound Lake leads hikers around the eastern side. The massif contains several high points including Helena Ridge (2,862 m (9,390 ft)), Stuart Knob (2,850 m (9,350 ft)) and Television Peak (2,970 m (9,744 ft)), the latter being named for the TV repeater located on top. Technicians use a helicopter rather than hiking the long ascent to the top.
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article Castle Mountain, which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike 4.0 International License (view authors).

Mount Robson Region


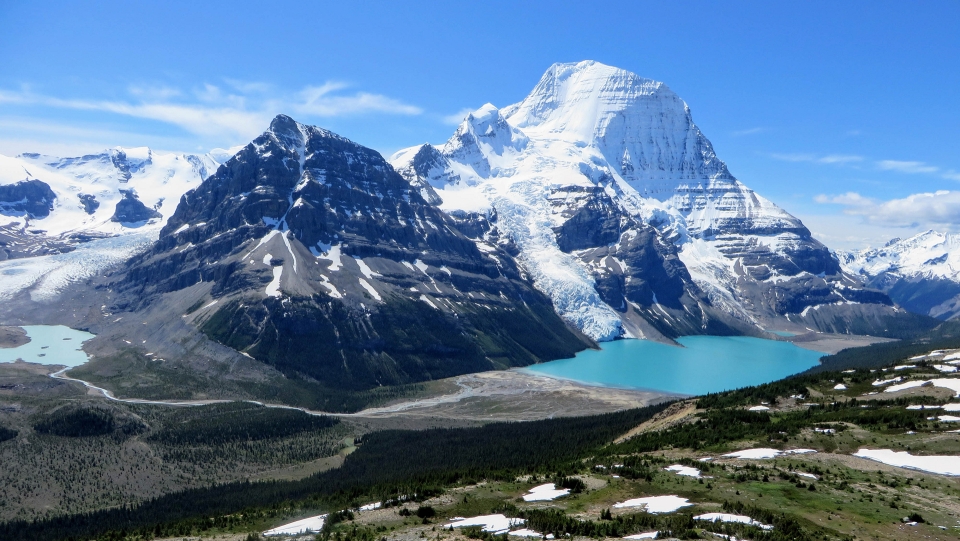
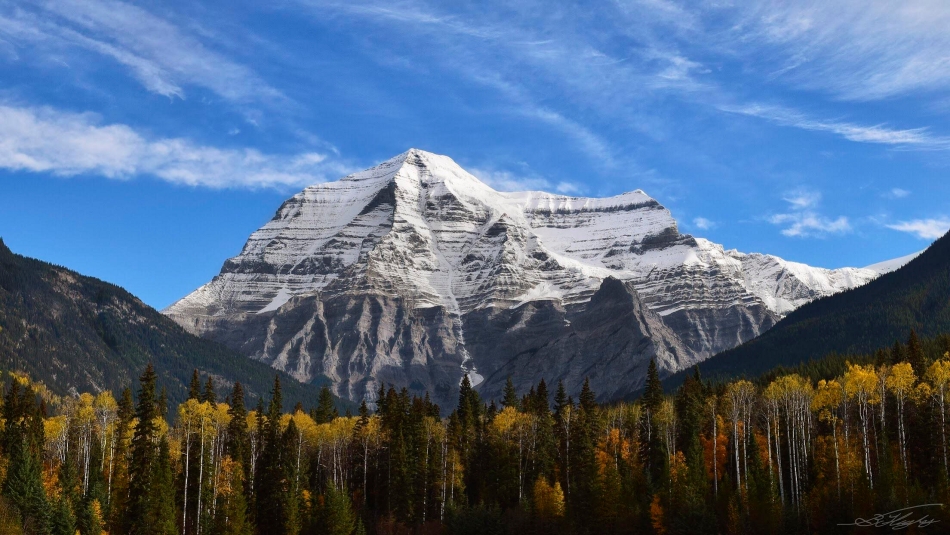
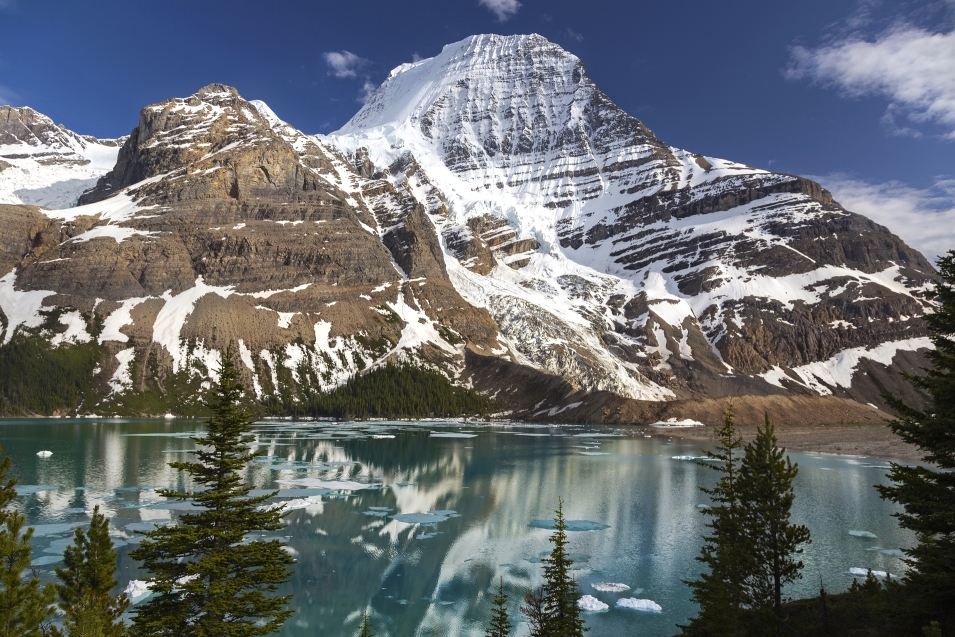
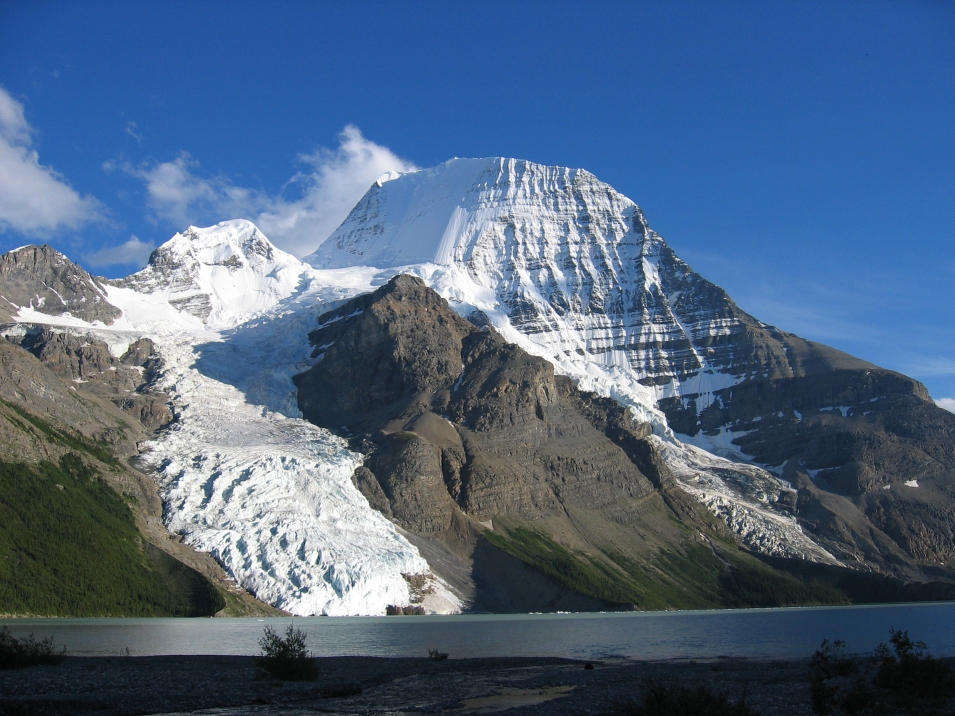
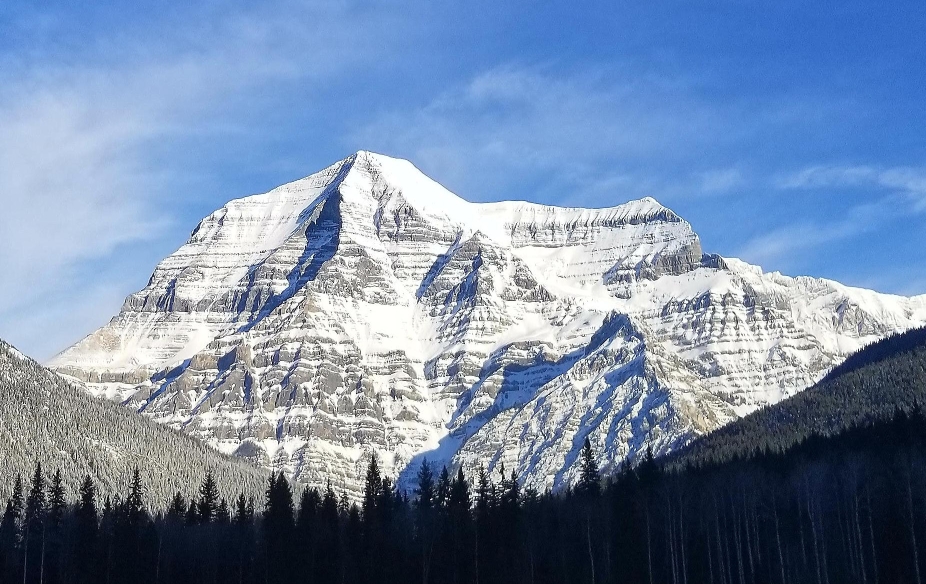
Mount Robson is the most prominent mountain in North America‘s Rocky Mountain range; it is also the highest point in the Canadian Rockies. The mountain is located entirely within Mount Robson Provincial Park of British Columbia, and is part of the Rainbow Range. Mount Robson is the second highest peak entirely in British Columbia, behind Mount Waddington in the Coast Range. The south face of Mount Robson is clearly visible from the Yellowhead Highway (Highway 16), and is commonly photographed along this route.
Mount Robson was likely named after Colin Robertson, who worked for both the North West Company and the Hudson’s Bay Company at various times in the early 19th century, though there was confusion over the name as many assumed it to have been named for John Robson, an early premier of British Columbia. The Texqa’kallt, a Secwepemc people and the earliest known inhabitants of the area, call it Yexyexéscen (striped rock), spelled in Dawson 1891 as Yuh-hai-has-kun, The Mountain of the Spiral Road.[6][7] Other unofficial names include Cloud Cap Mountain.[3]
Geography and climate
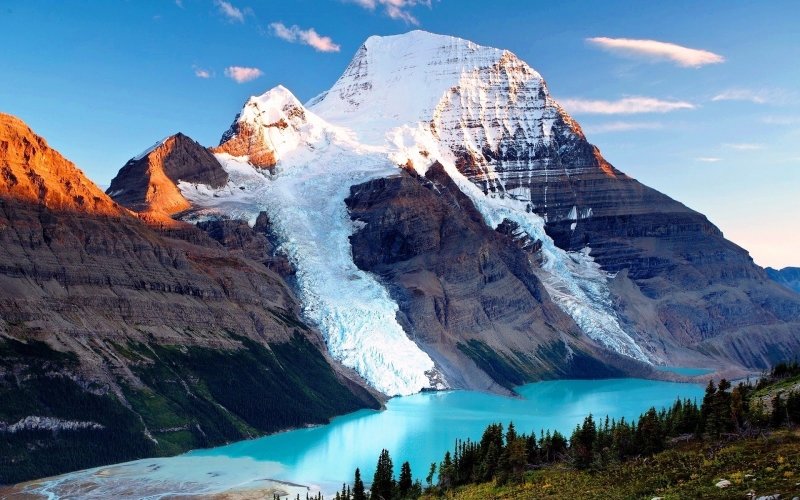
Mount Robson boasts great vertical relief over the local terrain. From Kinney Lake, the south-west side of the mountain rises 2,975 m (9,760 ft) to the summit. The north face of Mount Robson is heavily glaciated and 800 m (2,600 ft) of ice extends from the summit to the Berg Glacier.
The north face can be seen from Berg Lake, and reached by a 19 km (12 mi) hike. The lake is approximately 2 km long and lies at 1,646 m (5,400 ft) elevation. There are backcountry campgrounds at each end of the lake and a log shelter on its banks, named Hargreaves Shelter in honor of the Hargreaves family who operated the Mount Robson Ranch across the Fraser River from the mountain and who outfitted most of the early trips into Berg Lake. The Berg Glacier calves directly into the lake. The Robson Glacier, which fills the cirque and valley between Mount Robson and Mount Resplendent, in the early 1900s fed directly into both Berg lake and Adolphus Lake, straddling the Continental Divide and draining thus to both the Arctic and Pacific oceans via the Smoky and Robson Rivers, respectively. It since has receded more than 2 kilometres and is the source of the Robson River only. The peak of Mount Robson has a tundra climate (ET).[8]
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article Mount Robson, which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike 4.0 International License (view authors).

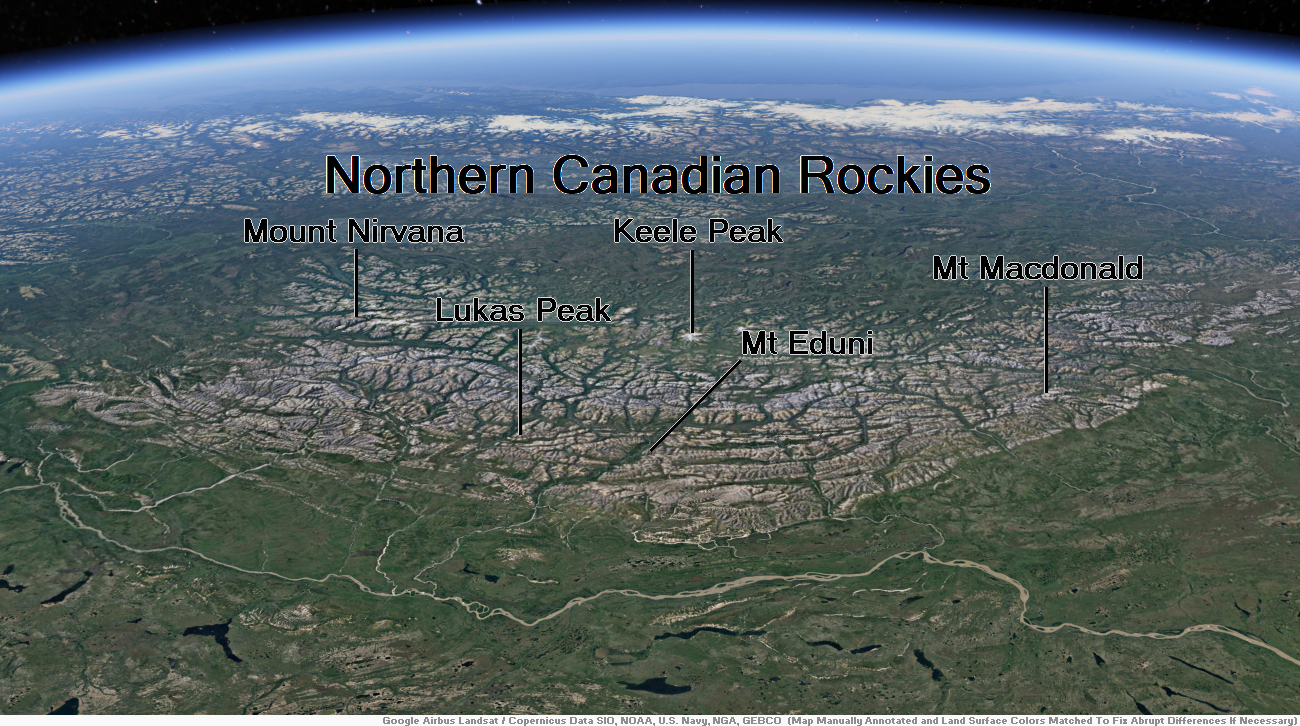
Northern Canadian Rockies Map
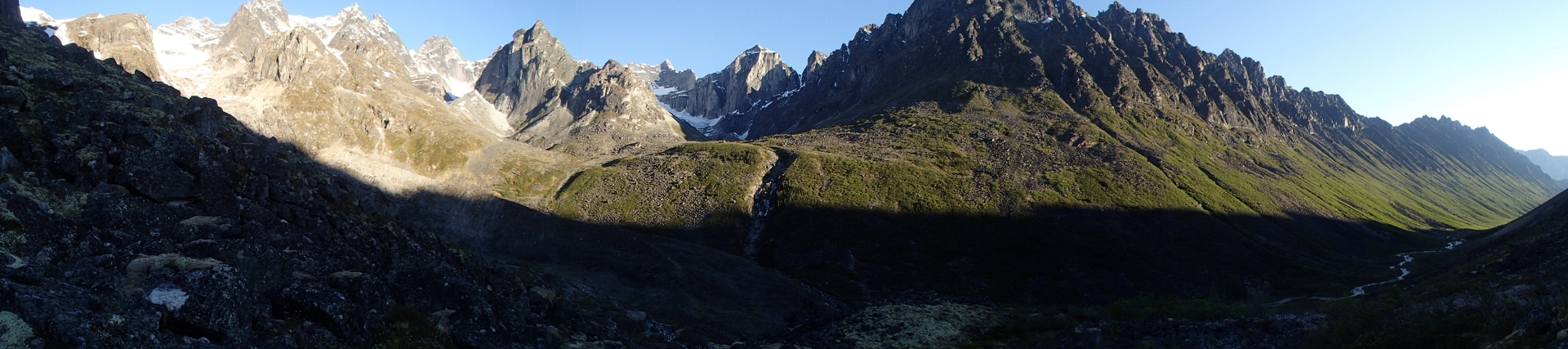
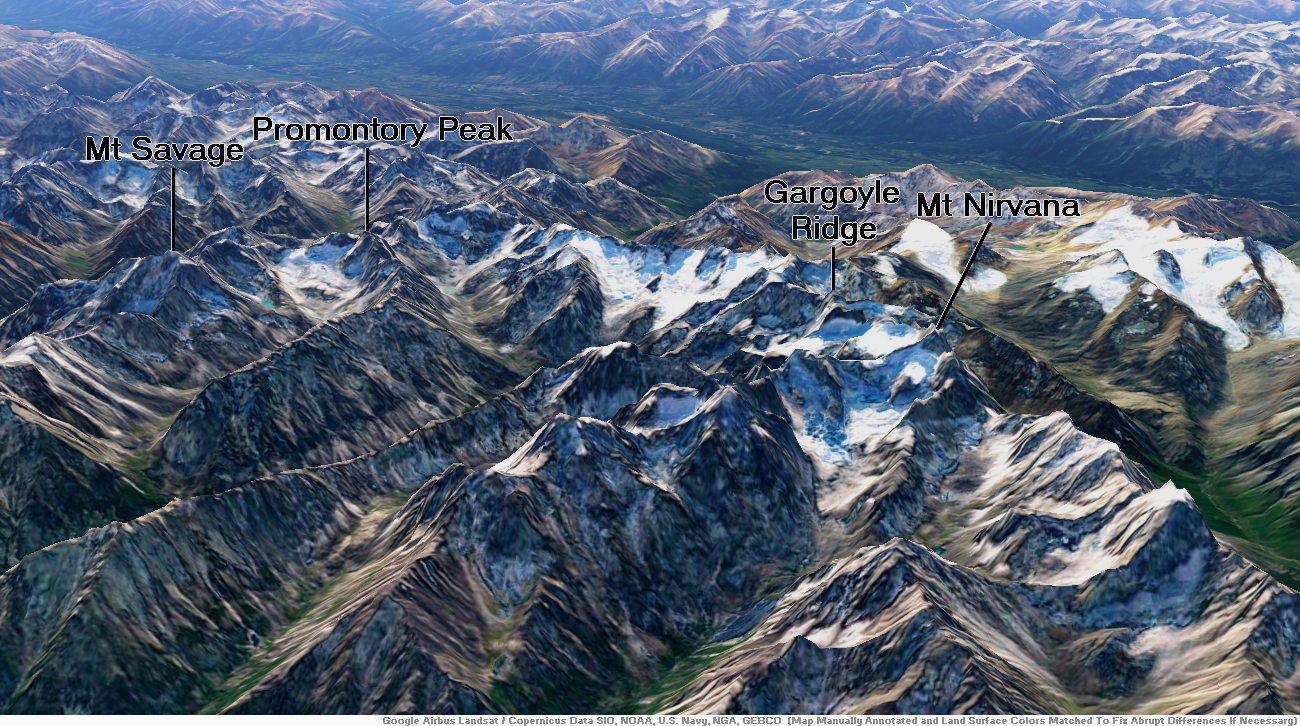
Mount Nirvana Region
Mount Nirvana Panoramic
Eric Gilbertson

Mount Nirvana, at 2,773 m (9,098 ft) is the unofficial name of the highest mountain in the Northwest Territories, Canada.[2][3] The mountain is a part of Nahanni National Park Reserve, the largest national park in the Northwest Territories.
History
Part of the Mackenzie Mountains, it was first climbed by Bill Buckingham and Lew Surdam in July 1965.[2][4] Buckingham gave the mountain the moniker of “Mount Nirvana” at that time.[5]
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article Mount Nirvana, which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike 4.0 International License (view authors).