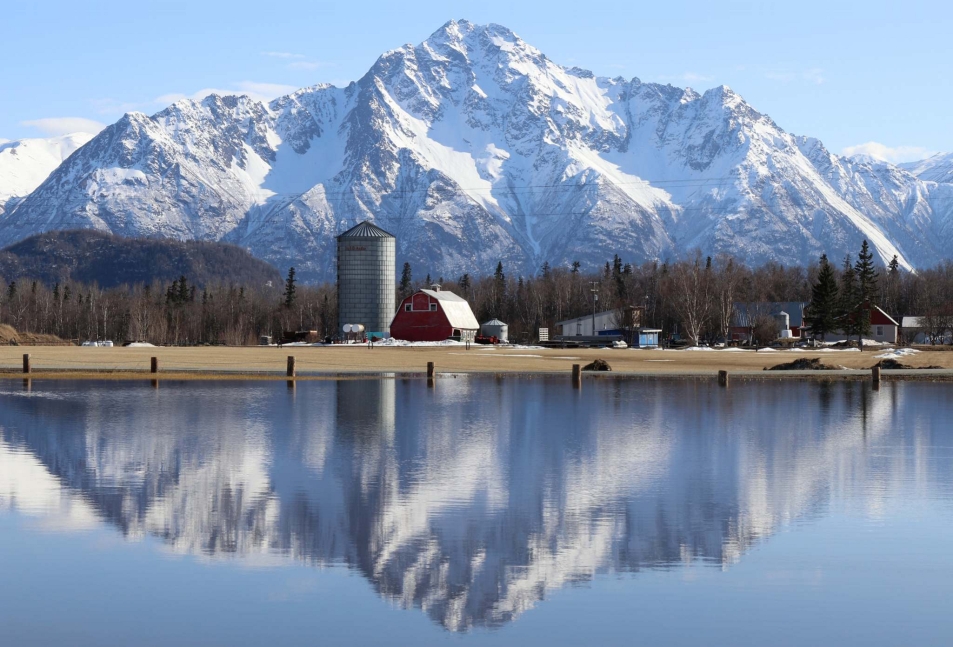
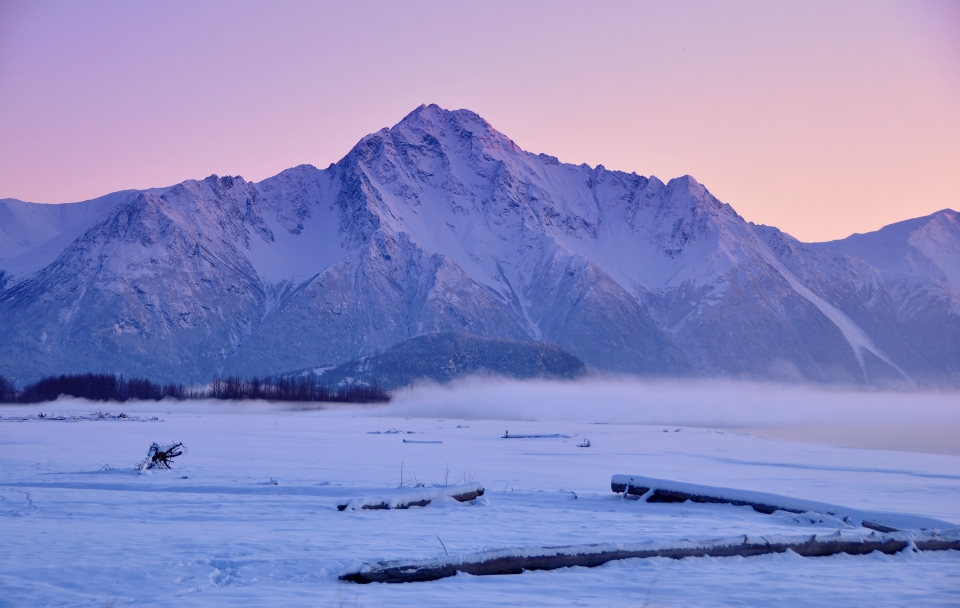
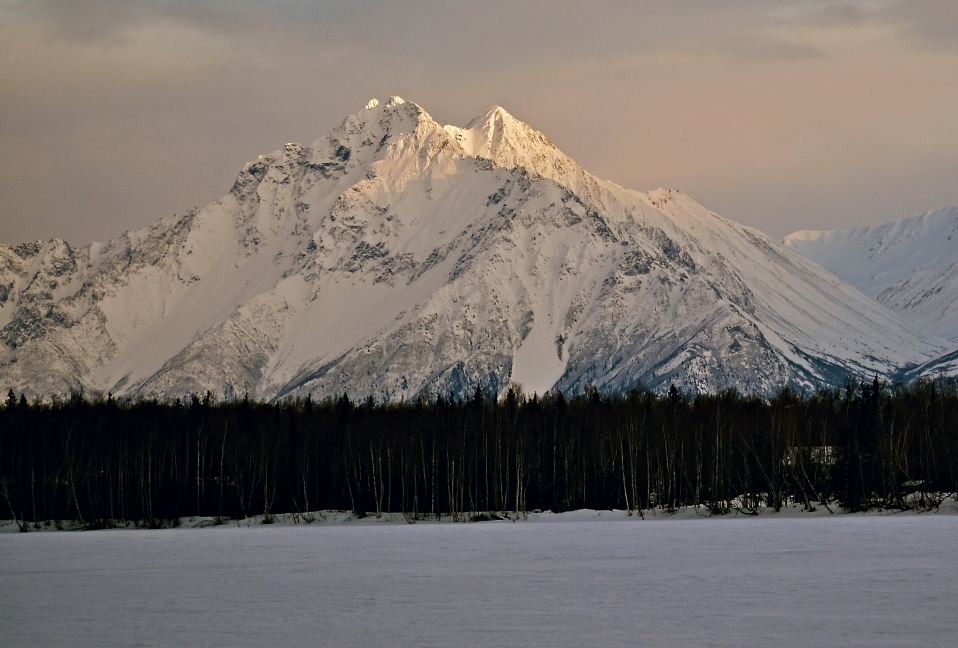
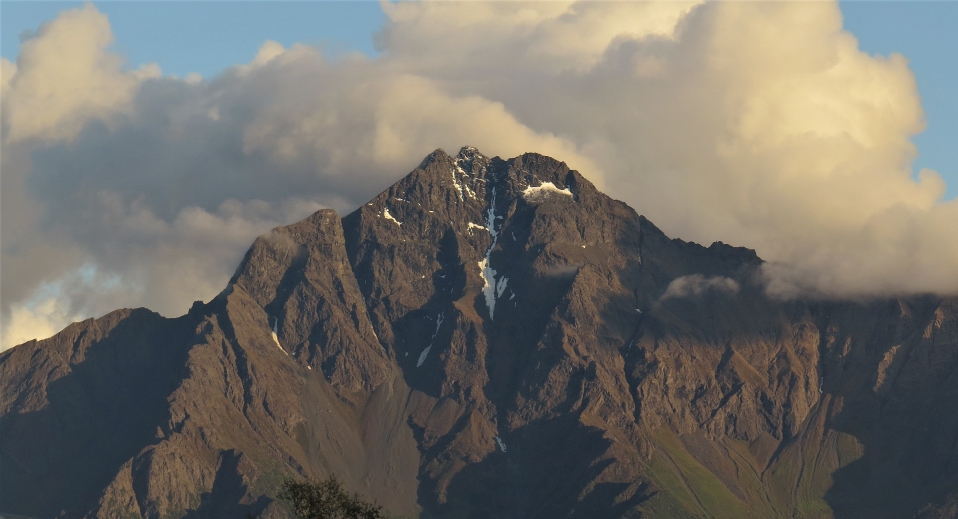
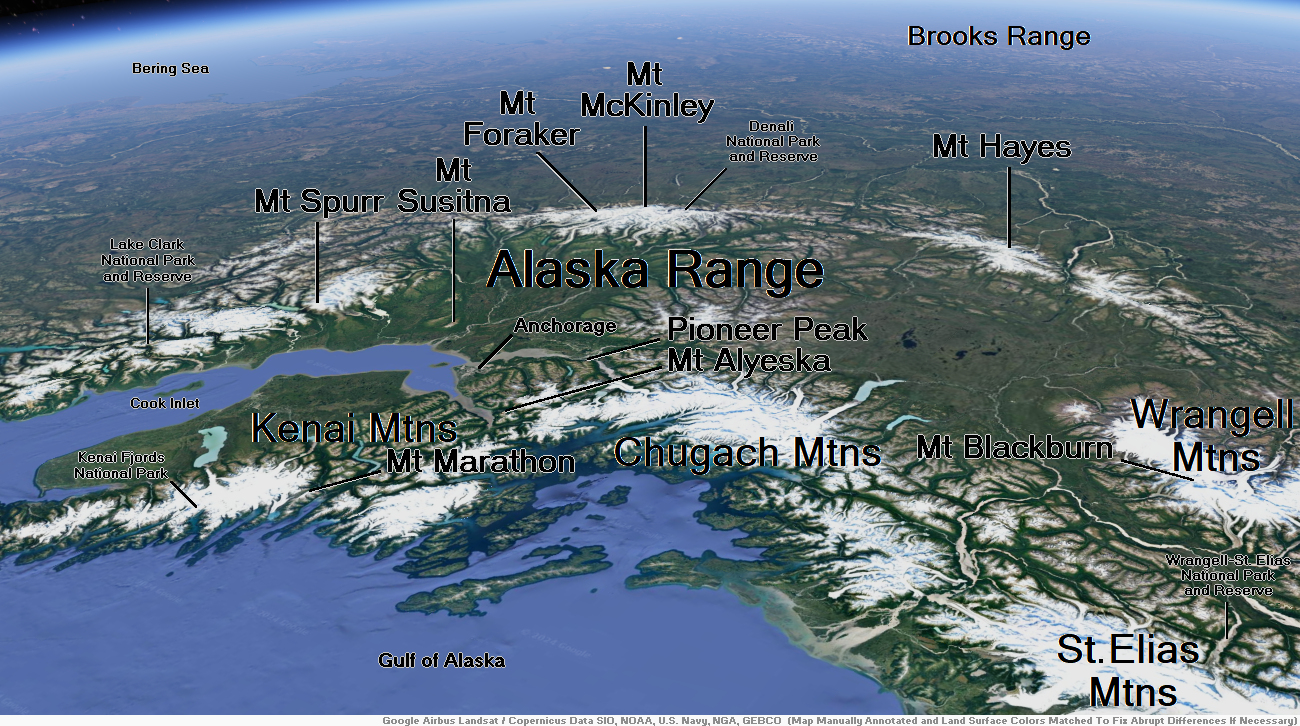
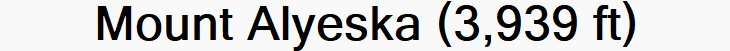Map of Alaska Range
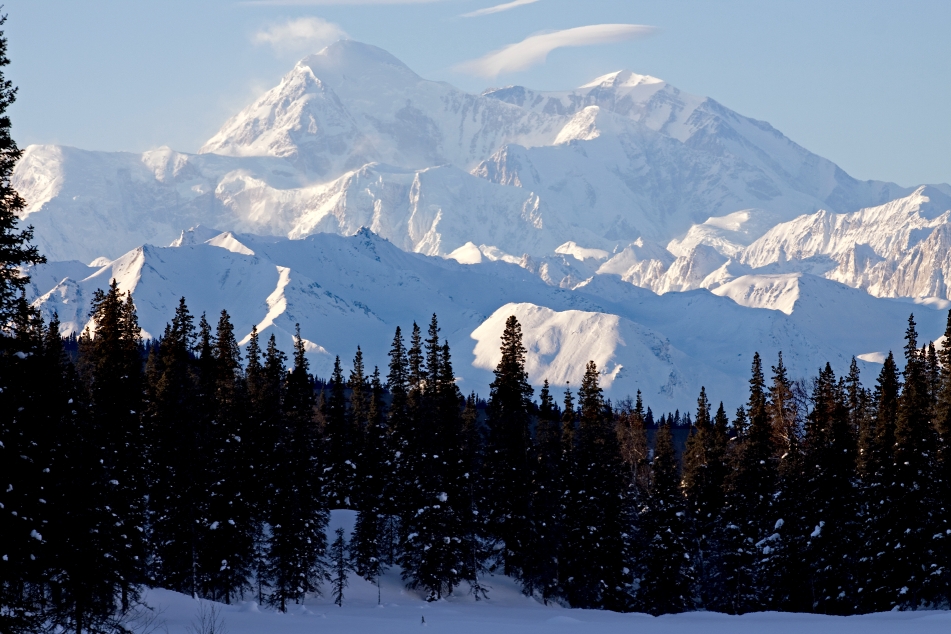
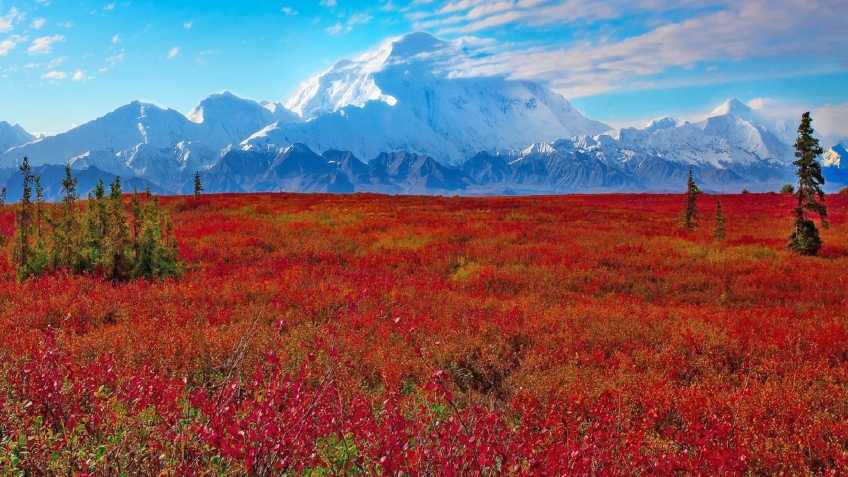
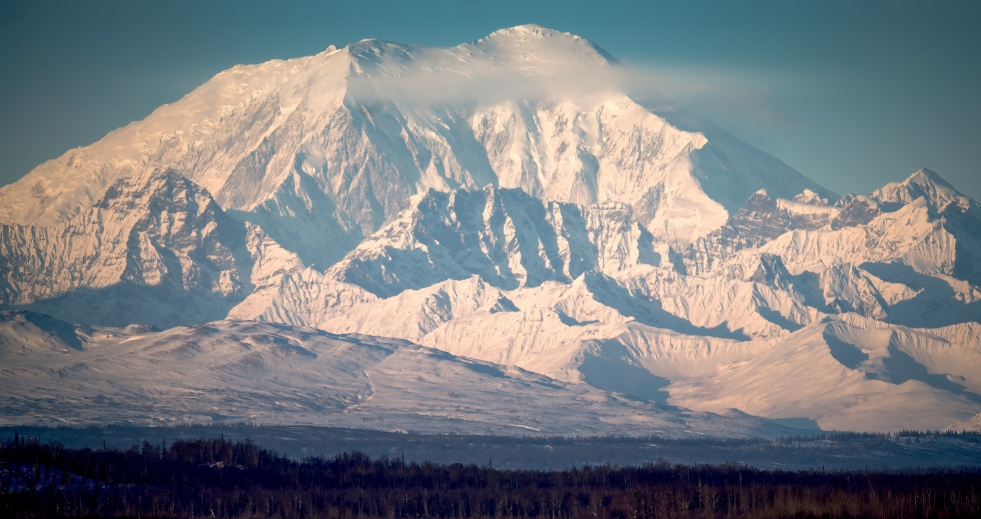
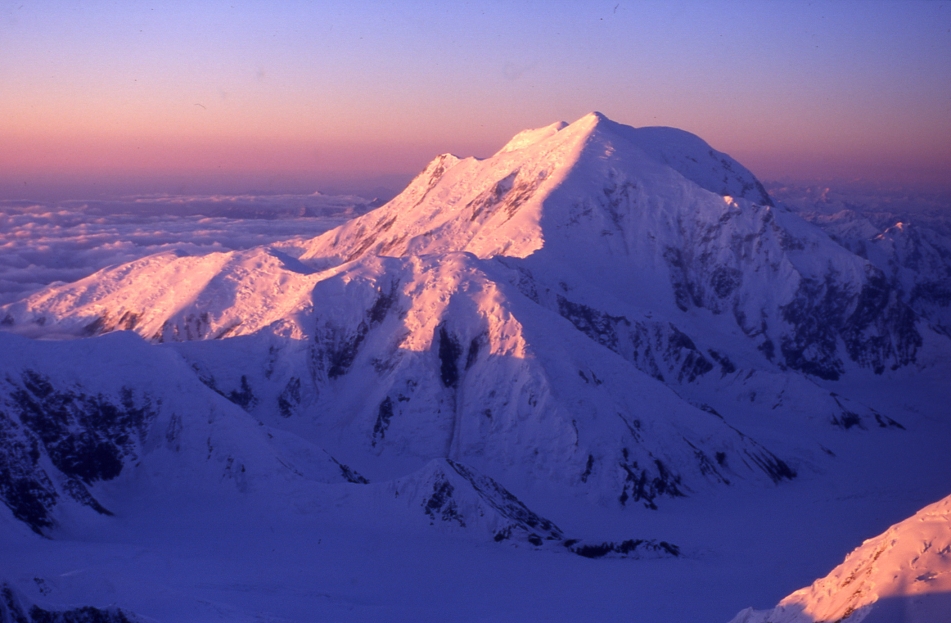
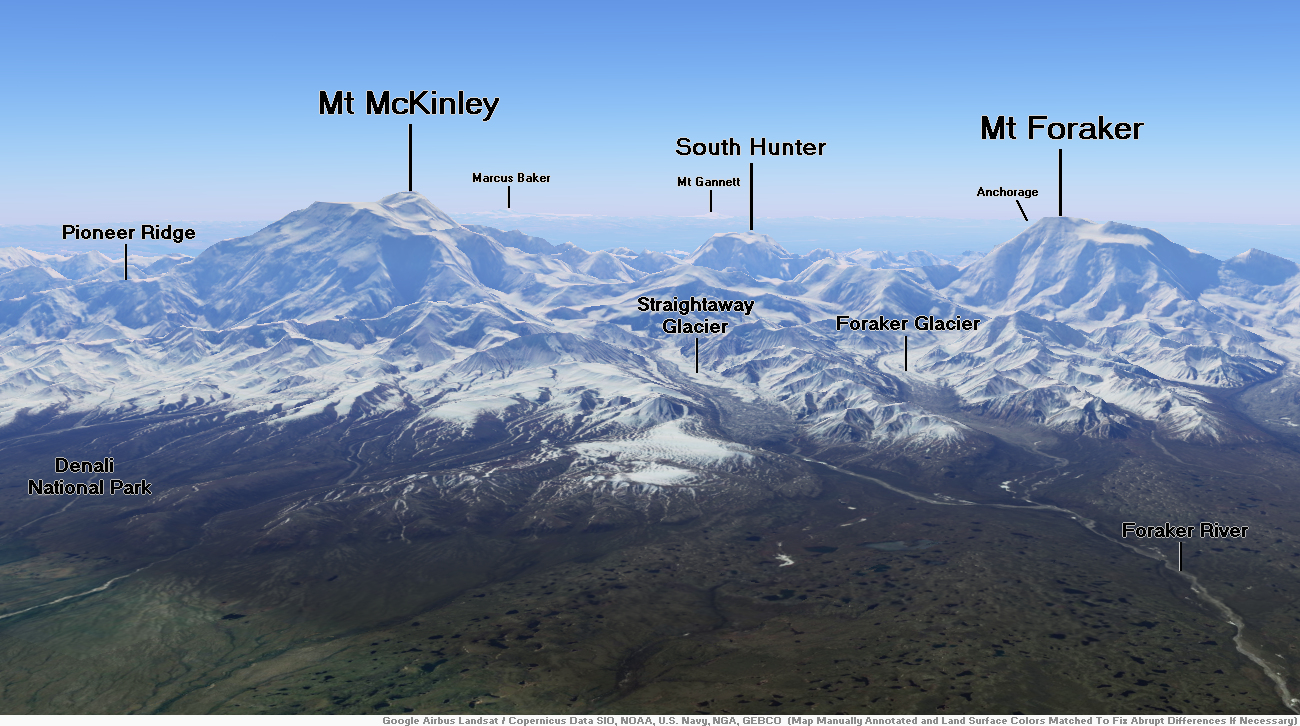
Mount McKinley Region 1
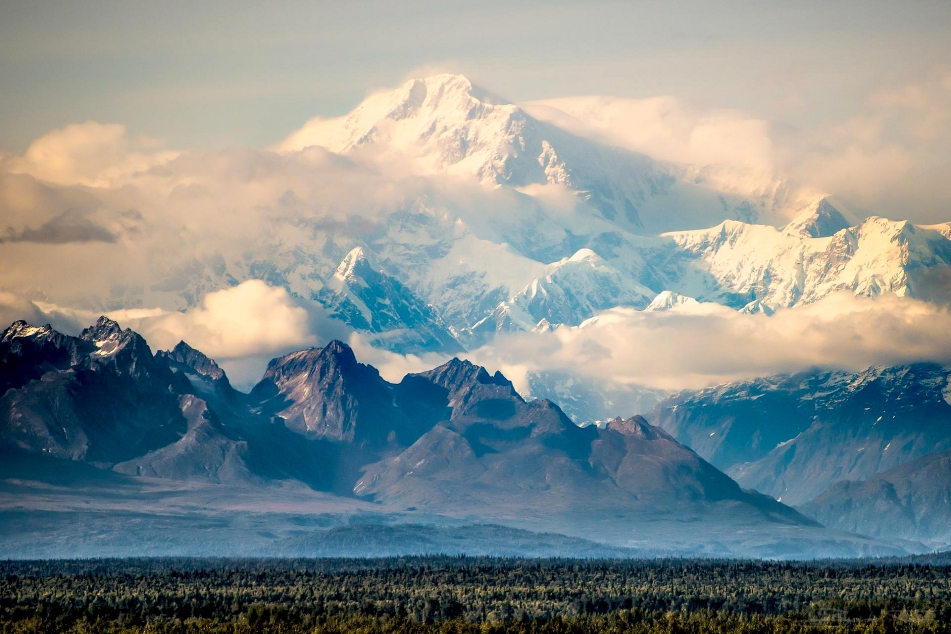
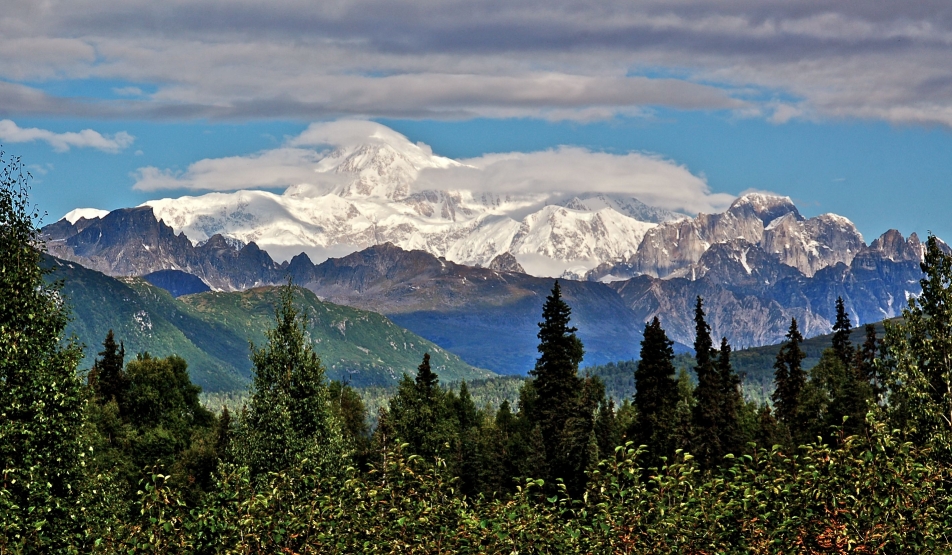
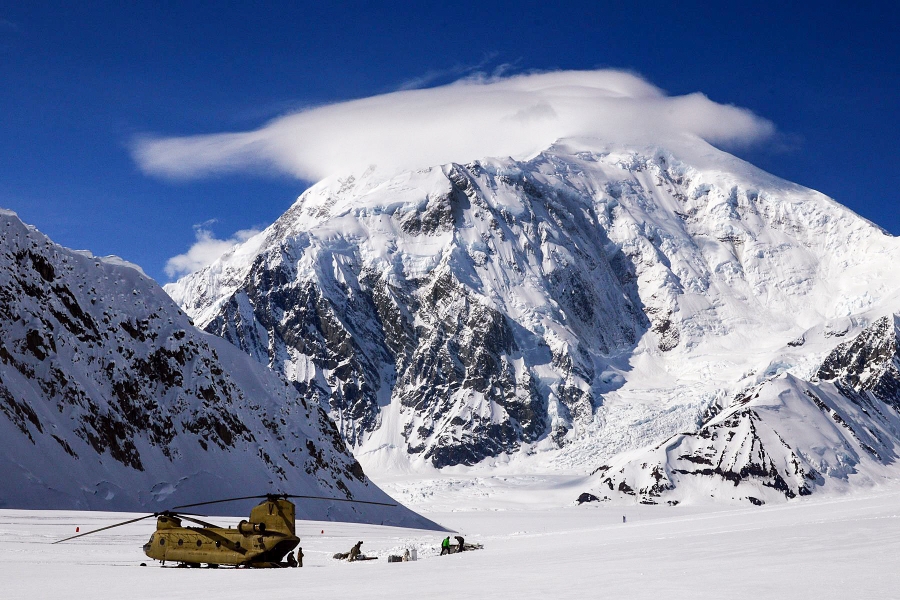
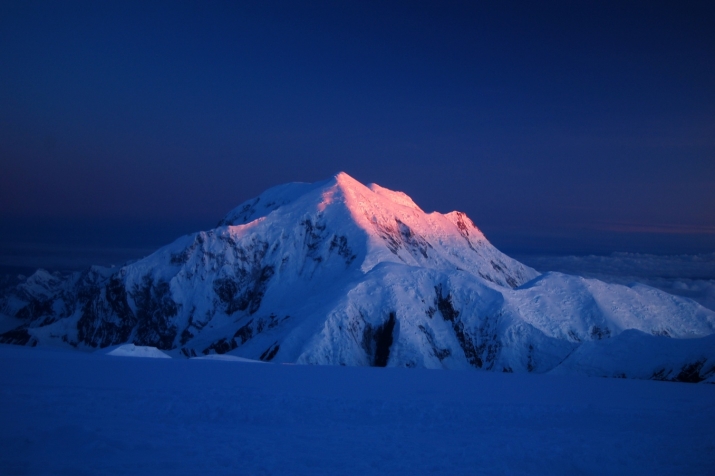
Mount McKinley Region 2


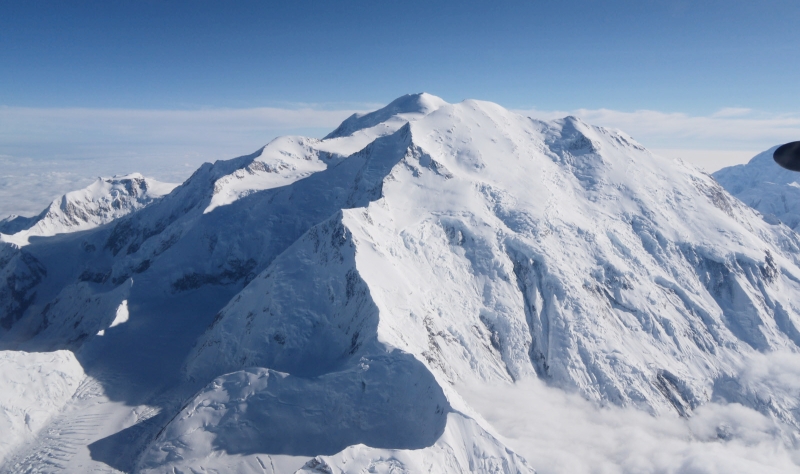
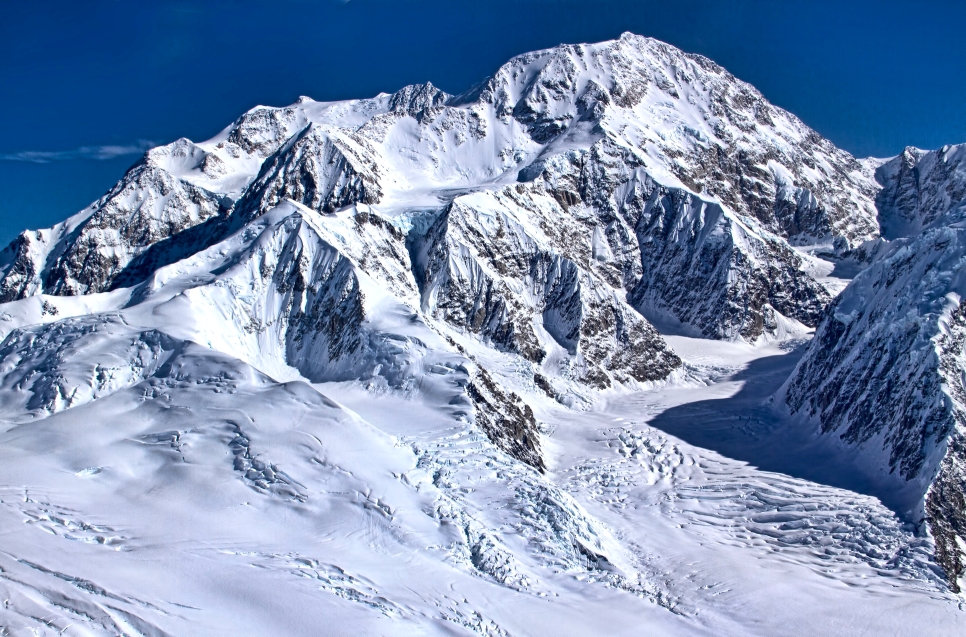
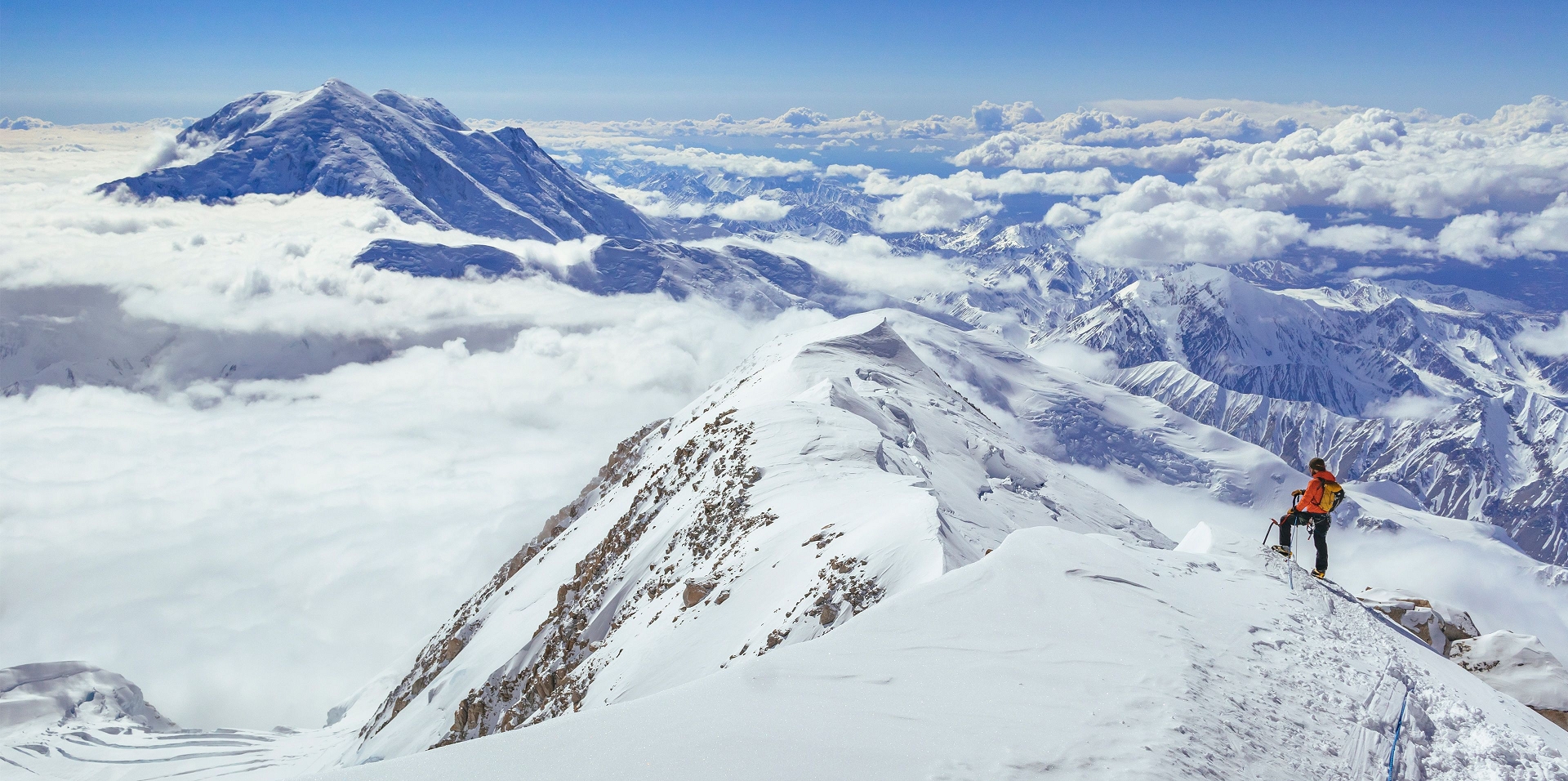
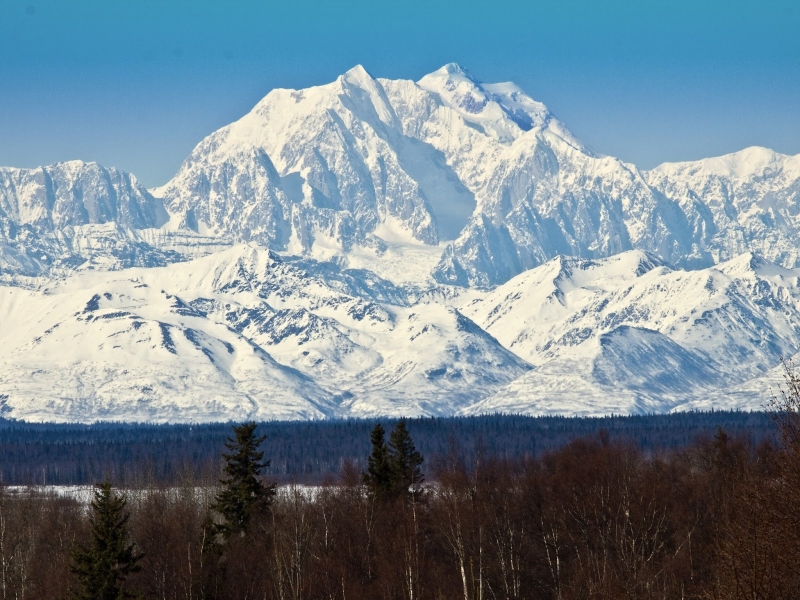
Mount McKinley Panoramic
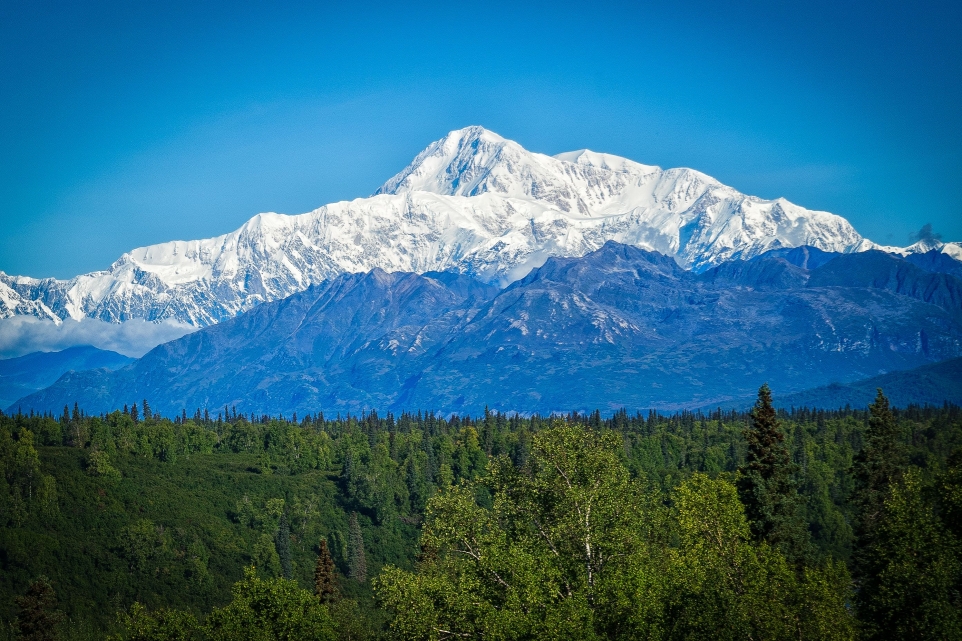
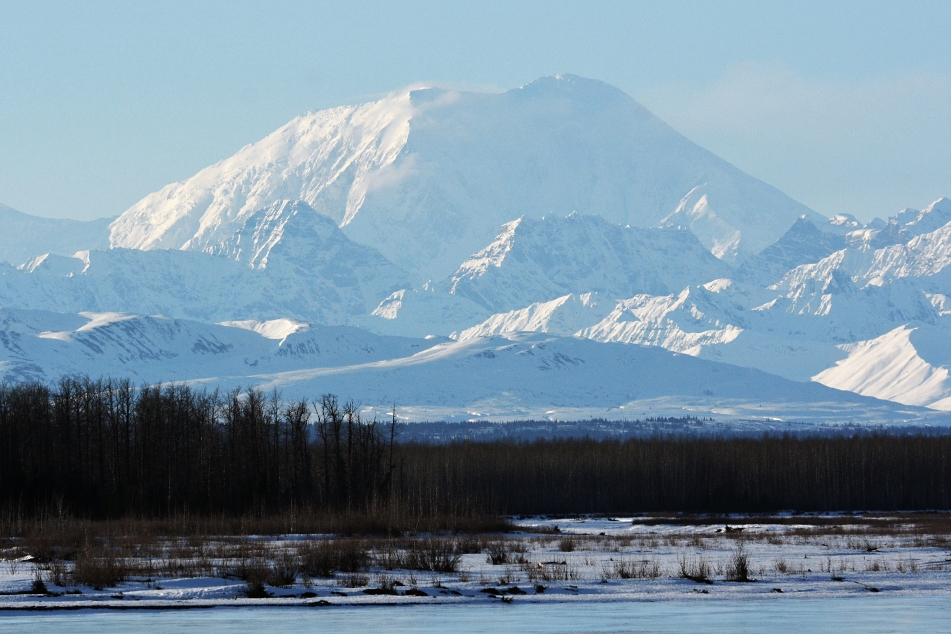
Mtnmichelle (iStock)

![]()
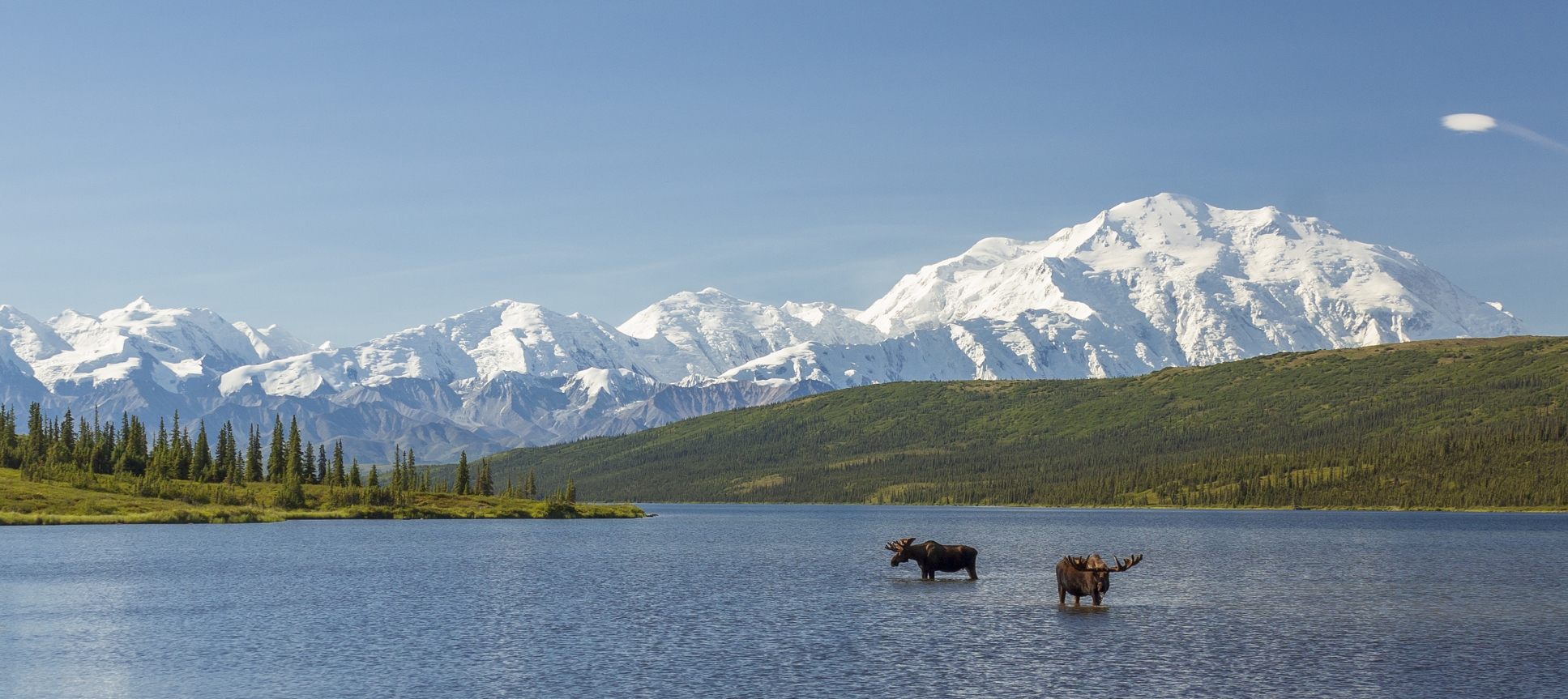
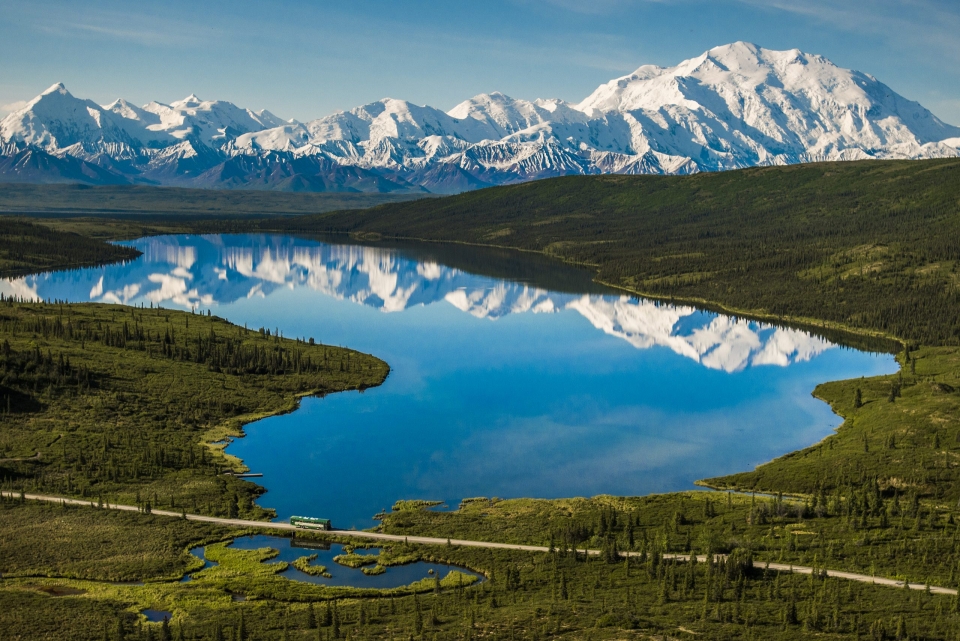
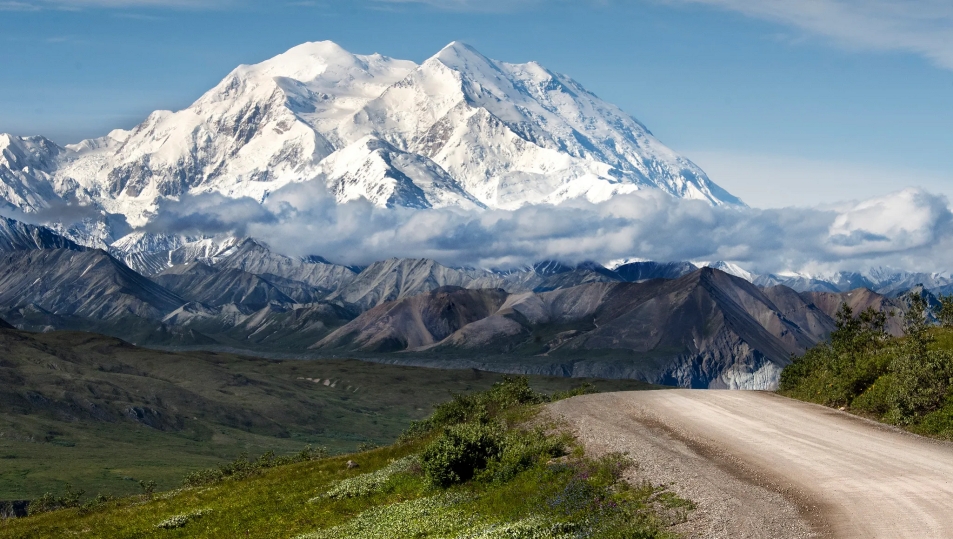
Denali (/dəˈnɑːli/),[5][6][7] federally designated as Mount McKinley,[8] is the highest mountain peak in North America, with a summit elevation of 20,310 feet (6,190 m) above sea level. It is the tallest mountain in the world from base-to-peak on land, measuring 18,000 ft (5,500 m).[9] With a topographic prominence of 20,194 feet (6,155 m)[3] and a topographic isolation of 4,621.1 miles (7,436.9 km),[3] Denali is the third most prominent and third-most isolated peak on Earth, after Mount Everest and Aconcagua. Located in the Alaska Range in the interior of the U.S. state of Alaska, Denali is the centerpiece of Denali National Park and Preserve.
The Koyukon people who inhabit the area around the mountain have referred to the peak as “Denali” for centuries. In 1896, a gold prospector named it “Mount McKinley” in support of then-presidential candidate William McKinley, who later became the 25th president; McKinley’s name was the official name recognized by the federal government of the United States from 1917 until 2015. In August 2015, 40 years after Alaska had done so, the United States Department of the Interior announced the change of the official name of the mountain to Denali.[9][10][11] On January 20, 2025, President Donald Trump signed an executive order requiring the Secretary of the Interior to revert this name change within 30 days of the order’s signing.[12] On January 23, 2025, the Department of the Interior changed the mountain’s official name back to Mount McKinley.[13][14]
In 1903, James Wickersham recorded the first attempt at climbing Denali, which was unsuccessful. In 1906, Frederick Cook claimed the first ascent, but this ascent is unverified and its legitimacy questioned. The first verifiable ascent to Denali’s summit was achieved on June 7, 1913, by climbers Hudson Stuck, Harry Karstens, Walter Harper, and Robert Tatum, who went by the South Summit. In 1951, Bradford Washburn pioneered the West Buttress route, considered to be the safest and easiest route, and therefore the most popular currently in use.[15]
On September 2, 2015, the U.S. Geological Survey measured the mountain at 20,310 feet (6,190 m) high,[1] 10 ft lower than the 20,320 feet (6,194 m) measured in 1952 using photogrammetry.
Geology and features
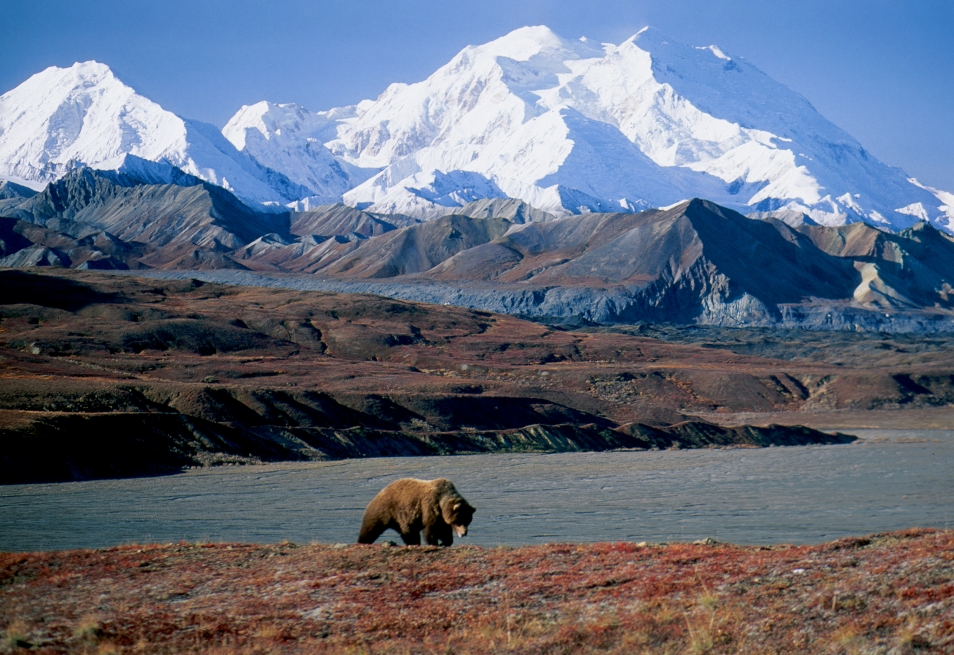
Denali is a granitic pluton, mostly pink quartz monzonite, lifted by tectonic pressure from the subduction of the Pacific Plate beneath the North American Plate; at the same time, the sedimentary material above and around the mountain was stripped away by erosion.[16][17] The forces that lifted Denali also caused many deep earthquakes in Alaska and the Aleutian Islands. The Pacific Plate is seismically active beneath Denali, a tectonic region that is known as the “McKinley cluster”.[18]
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article Denali, which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike 4.0 International License (view authors).

Mount Foraker Panoramic
Mohammed Ibrahim

![]()
Mount Foraker is a 17,400-foot (5,304 m) mountain in the central Alaska Range, in Denali National Park, 14 mi (23 km) southwest of Denali. It is the second highest peak in the Alaska Range, and the third highest peak in the United States. It rises almost directly above the standard base camp for Denali, on a fork of the Kahiltna Glacier also near Mount Hunter in the Alaska Range.
Its north peak was first climbed on August 6, 1934, and its higher south peak was climbed four days later on August 10, by Charles Houston, T. Graham Brown, and Chychele Waterston, via the west ridge.[3][4]
Name
Mount Foraker was named in 1899 by Lt. J. S. Herron after Joseph B. Foraker, then a sitting U.S. Senator from Ohio.[5]
The Koyukon native peoples in the Lake Minchumina area had a broadside view of the mountains and thus gave distinctive names to both Foraker and Denali. According to Hudson Stuck, the Koyukon had two names for Mount Foraker: Sultana meaning “the woman” and Menlale meaning “Denali’s wife”.[3] The Denaʼina of the Susitna River valley called the mountain Be’u meaning his wife (Denali) and the Lower Tanana Athabascans to the north are reported to have had the same name (Denali) for Mt. Foraker as they had for Denali (previously Mount McKinley), and it appears that the names were not applied to individual peaks but instead to the Denali massif. The mountain, along with Denali, was called Bolshaya Gora (“big mountain”) in Russian.[citation needed]
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article Mount Foraker, which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike 4.0 International License (view authors).

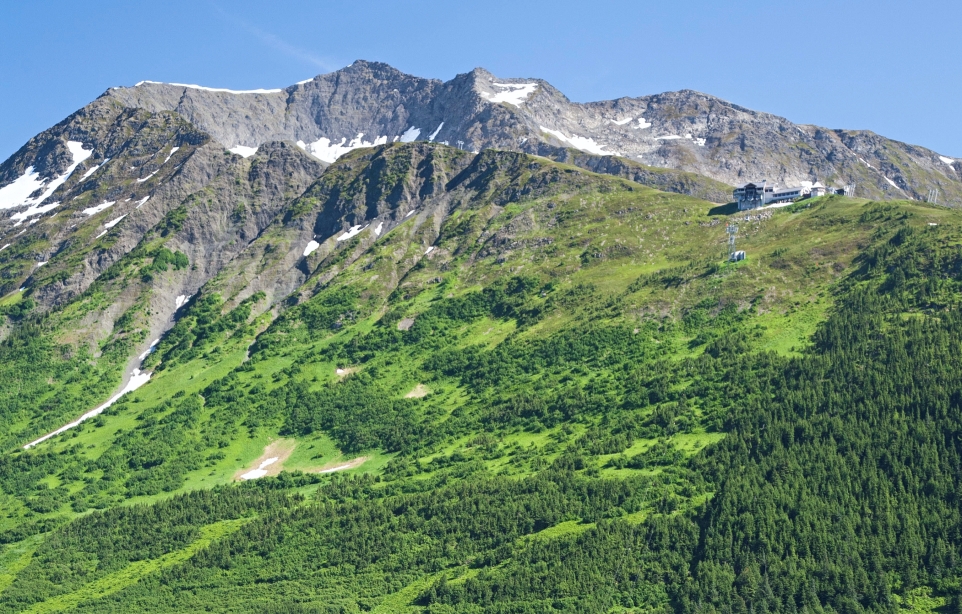
Mount Alyeska Region

![]()

Alyeska Resort is a ski resort in the Girdwood area of Anchorage, Alaska, approximately 30 miles (48 km) from downtown Anchorage. Mount Alyeska is part of the Chugach mountain range and the Alyeska Resort is the largest ski area in the state. It includes the mountaintop Mt. Alyeska Roundhouse, which is listed on the National Register of Historic Places.
Facilities and terrain
The Alyeska Ski Corporation was founded in 1954, and the first chairlift and day lodge were opened in 1959. The Roundhouse ski lodge and ski patrol station at the top of the mountain began construction in 1960. It is an octagonal building. Still standing, it was listed on the National Register of Historic Places as “Mt. Alyeska Roundhouse” in 2003, and now houses a museum to local ski history.[1][2]
Currently, Alyeska has five chairlifts, one high-speed aerial tramway, and two Magic Carpets. Of the five chairlifts, one is co-owned by Alyeska and the Tanaka Foundation (Chair 5). Chairs 6 and 4 are high-speed detachable quads, while Chairs 7 and 3 are normal quads. Chair 4 was updated to a high speed quad in 2012. A sixth chairlift, Chair 1, was removed from service in the summer of 2017.
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article Alyeska Resort, which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike 4.0 International License (view authors).

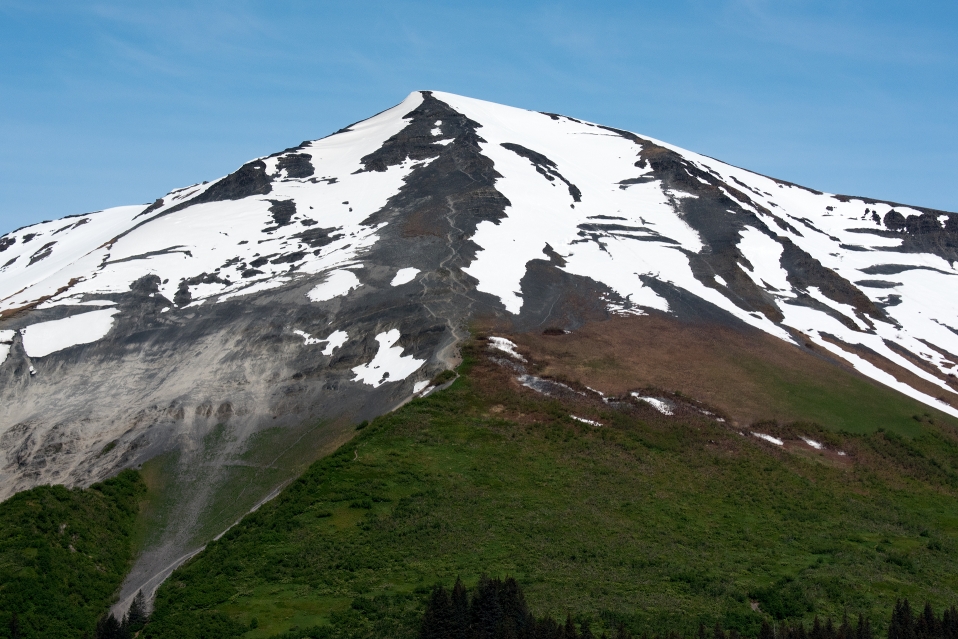
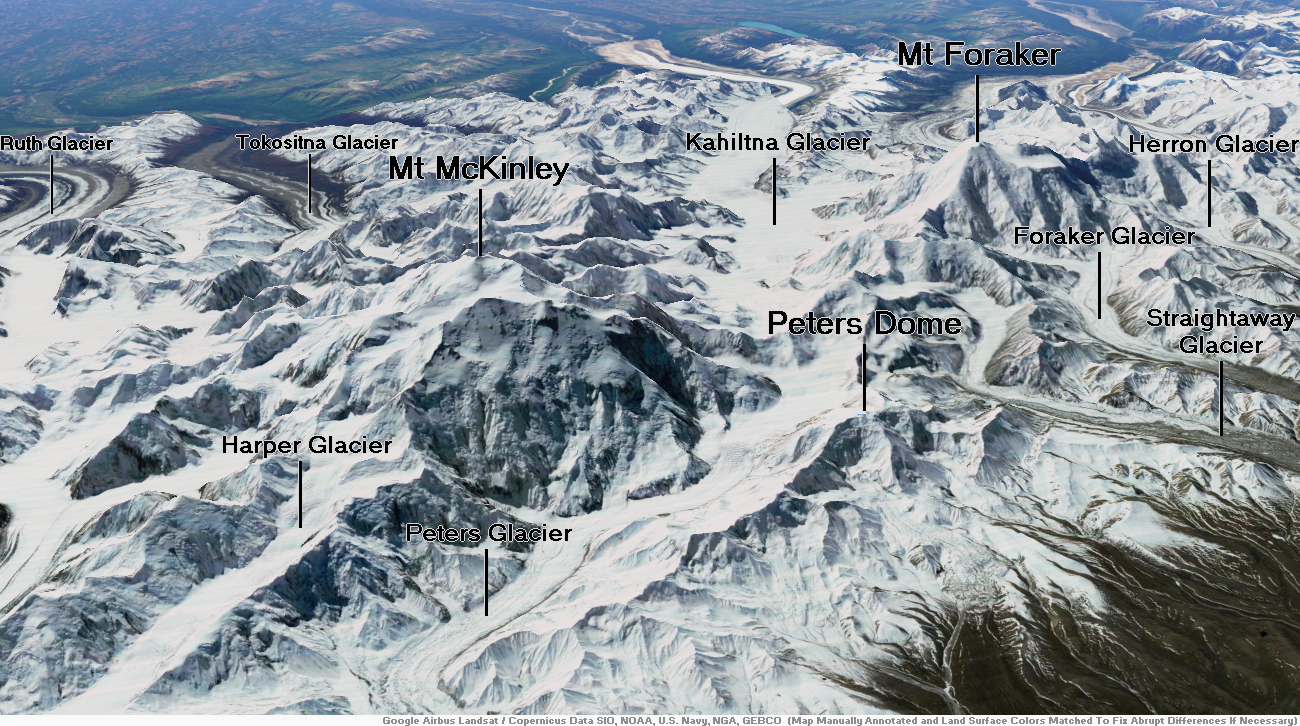
Mount Marathon Region

Mount Marathon, or officially Marathon Mountain, is a 4,826-foot (1,471 m) mountain summit directly west of Seward in the Kenai Mountains in the U.S. state of Alaska. The peak is situated in Chugach National Forest, rising above Resurrection Bay, 2.35 mi (4 km) south of Mount Benson, and 2 mi (3 km) north of Bear Mountain. The namesake of the mountain is the Mount Marathon Race held every Fourth of July.[2]
Climate
Based on the Köppen climate classification, Mount Marathon is located in a subarctic climate zone with long, cold, snowy winters, and mild summers.[3] Temperatures can drop below −20 °C with wind chill factors below −30 °C. This climate supports a spruce and hemlock forest on the lower slopes. The months May and June offer the most favorable weather for viewing.
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article Mount Marathon, which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike 4.0 International License (view authors).

Resurrection Peaks is a 4,727-foot (1,441 m) mountain ridge located in the Kenai Mountains, on the Kenai Peninsula, in the U.S. state of Alaska. The peaks are situated in Chugach National Forest, 3.3 mi (5 km) north of Mount Benson, 3.5 mi (6 km) south of Mount Ascension, and 5 mi (8 km) north of Seward, Alaska. These peaks, marked 4712′ and 4665′ on the USGS map, together with their ridges and glacier form a distinct group. The peaks overlook the mouth of Resurrection River into Resurrection Bay, and take their name from the bay named since 1792, and the river since 1898. Resurrection Peaks’ name was officially adopted in 1969 by the United States Geological Survey.[3]
Climate
Based on the Köppen climate classification, Resurrection Peaks are located in a subarctic climate zone with long, cold, snowy winters, and mild summers.[4] Temperatures can drop below −20 °C with wind chill factors below −30 °C. This climate supports a spruce and hemlock forest on the lower slopes. The months May and June offer the most favorable weather for viewing.
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article Resurrection Peaks, which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike 4.0 International License (view authors).

Pioneer Peak Region


![]()
Pioneer Peak (Ahtna: Tnel’aay; Dena’ina: Dnal’iy) is a 6,398-foot (1,950 m) mountain in the Chugach Mountains in the U.S. state of Alaska. Located beside the Knik River just nine miles (14.5 km) south of Palmer and about six miles outside the Municipality of Anchorage limits, it is a prominent landmark in the Matanuska-Susitna Valley, as well as a popular hiking destination. Its Ahtna name means “the object is standing still” and its Dena’ina name means “the one that watches us“.[3] The name was given in 1939 in honor of the pioneers of the Matanuska agricultural colony of the mid-1930s.[2] The Pioneer Ridge Trail leads up the eastern shoulder, beginning below 200′, it allows access to the South summit. The North summit, and true summit of Pioneer Peak does not have a trail, and advanced mountaineering techniques are required. The first ascent of this peak was made June 1936 by Vernon Haik and John Wolffe via the Northwest Face.[4]
Climate
Based on the Köppen climate classification, Pioneer Peak is located in a subarctic climate zone with long, cold, snowy winters, and mild summers.[5] Weather systems coming off the Gulf of Alaska are forced upwards by the Chugach Mountains (orographic lift), causing heavy precipitation in the form of rainfall and snowfall. Temperatures can drop below −20 °C with wind chill factors below −30 °C. The months May through June offer the most favorable weather for climbing or viewing.
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article Pioneer Peak (Alaska), which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike 4.0 International License (view authors).

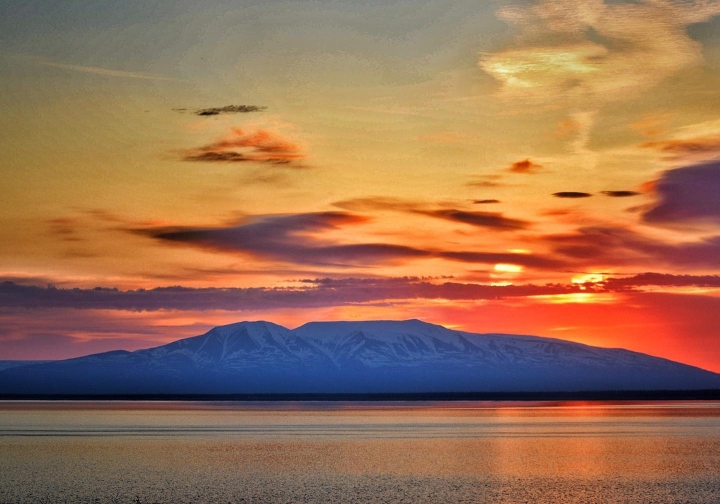
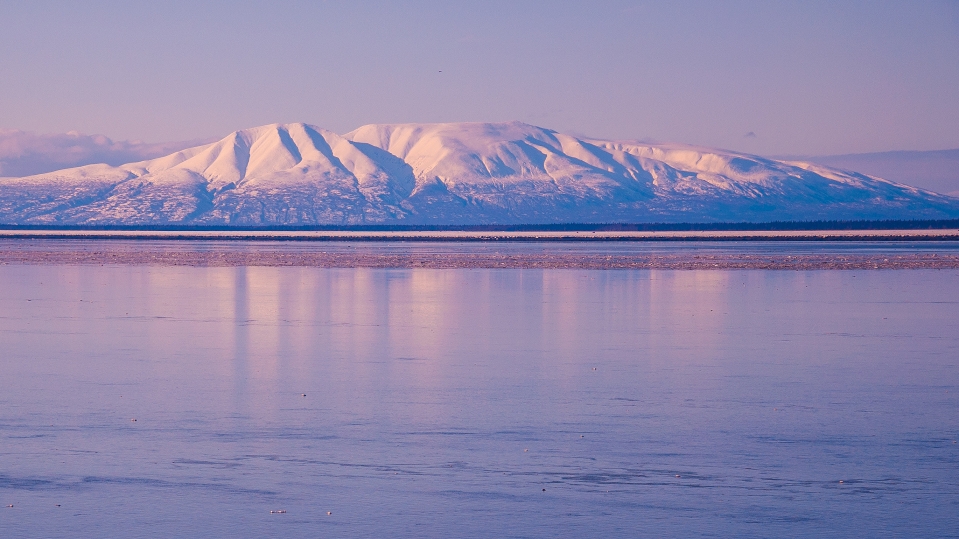
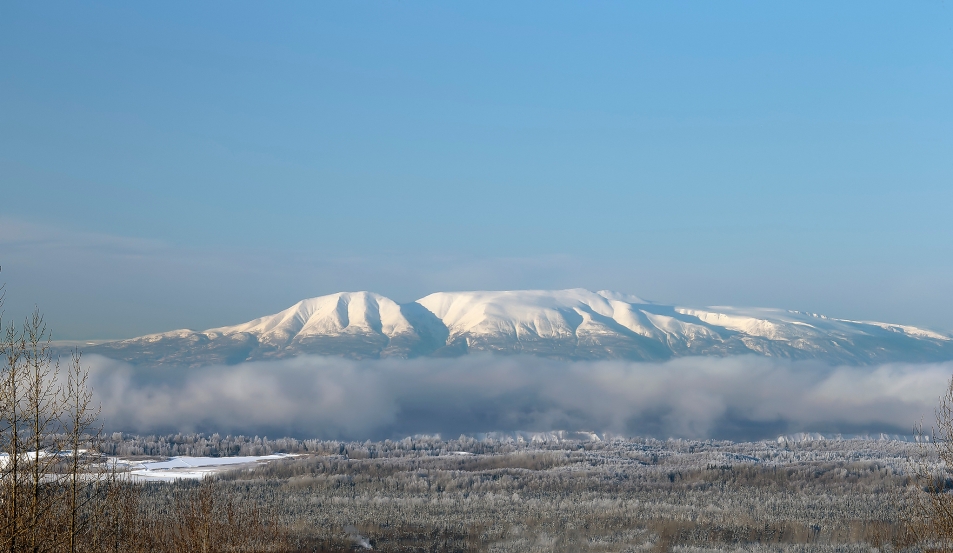
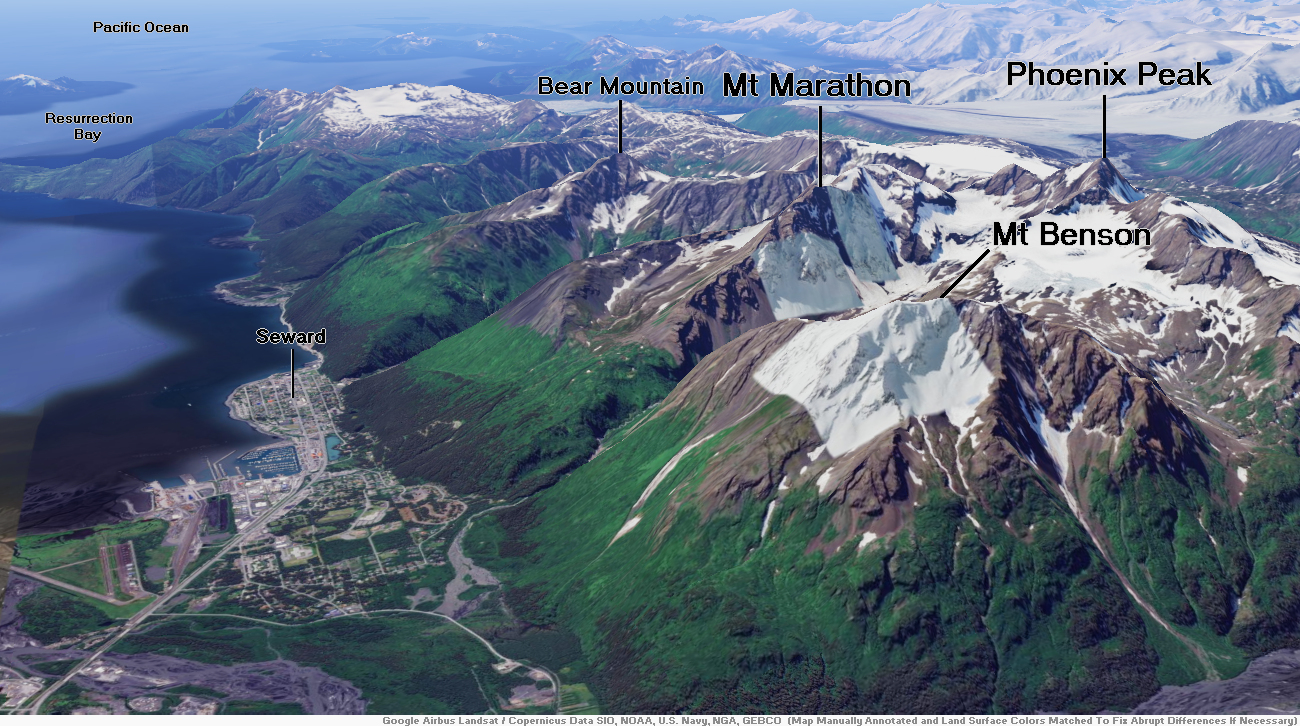
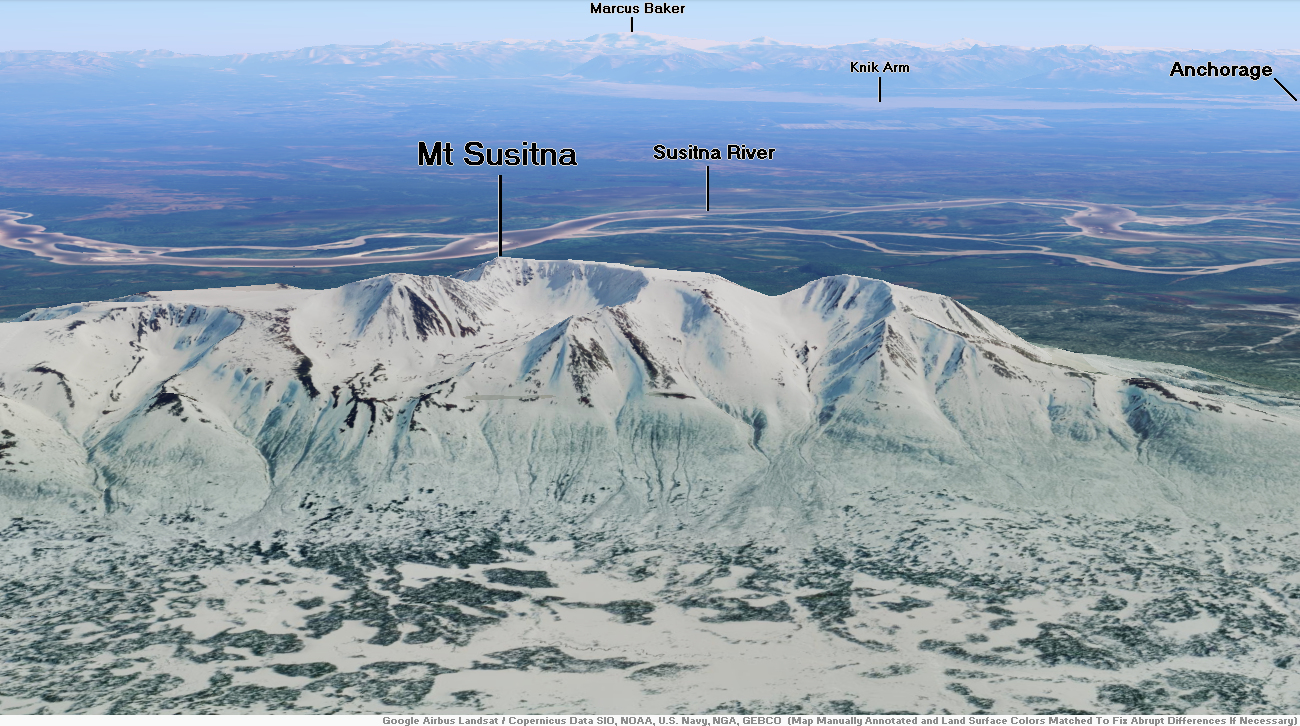
Mount Susitna Region

![]()
Mount Susitna, also known as Sleeping Lady, (Dena’ina: Dghelishla) is a 4,396-foot (1,340 m) mountain in the U.S. state of Alaska. It is located on the west bank of the lower Susitna River, about 33 miles (53 km) northwest of Anchorage, Alaska.[1] The mountain is a prominent landmark in the Anchorage area and can be seen across the Knik Arm of the Cook Inlet from most of the city, especially at higher elevations.
Etymology and Alaska Native names
The mountain’s Dena’ina name is Dghelishla, meaning “Little Mountain”; in English it was simply named for the Susitna River which means Sandy River.[1] “Dinglishna” in Alaska is a similar word which means “Little Ridge that Extends”.[2]
Legends
Mount Susitna is often called Sleeping Lady for its resemblance to a recumbent woman. The mountain is associated with a local legend in which a woman belonging to a race of giants vows to sleep until her beloved comes back from battle.[3] The first known printing of the local legend was written by Nancy Lesh and published in 1962.[3] A retelling of the legend was published in a 1994 picture book by Ann Dixon. Dixon and her publisher were sued for their version of the story, but a judge ruled that the story had become a legend, and was therefore uncopyrightable.[3][4]
In “A Dena’ina Legacy,” Dena’ina elder Peter Kalifornsky tells the story of the Mountain People who gathered at Susitna, and a giant lady who said she would lie down by the river she loved to become Susitna Mountain. Her relatives followed, Kalifornsky said, to become Mount Redoubt, Mount Iliamna and the Chigmit Mountain Range. Another wandered inland to become Denali.[4]
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article Mount Susitna which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike 4.0 International License (view authors).